Ultimate Guide To Even Numbers 1 To 100: Facts, Patterns, And Uses
Even numbers are a fundamental part of mathematics and play a significant role in various aspects of daily life. When we talk about even numbers 1 to 100, we refer to numbers divisible by 2 without leaving a remainder. These numbers form an essential sequence in arithmetic, helping us understand mathematical concepts like division, grouping, and symmetry. Whether you're a student, a teacher, or simply curious about numbers, understanding even numbers can deepen your appreciation for the logical beauty of math.
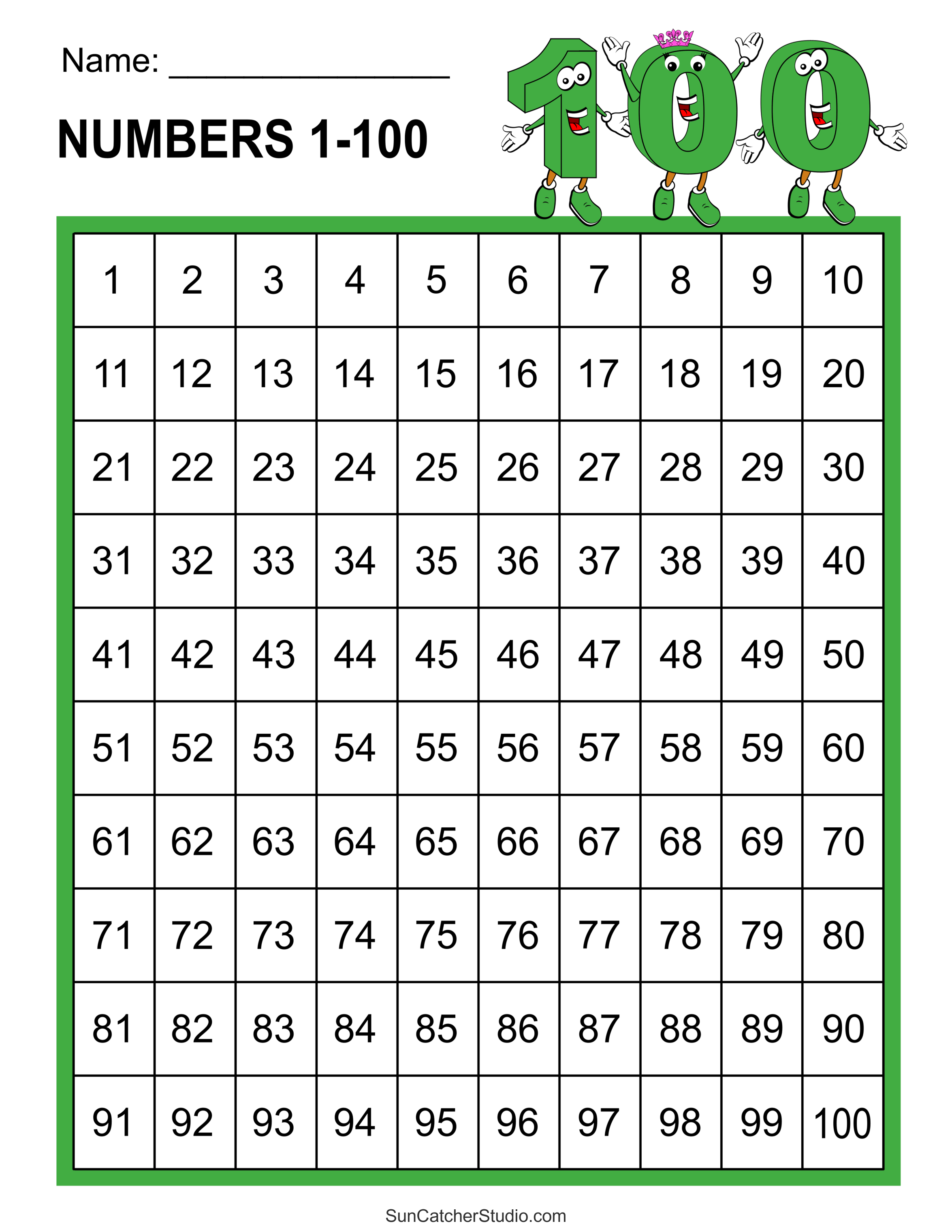
From the first even number (2) to the last even number within the range (100), this sequence highlights regularity and balance. Even numbers 1 to 100 include 50 numbers: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and so on, up to 100. Each of these numbers shares a common trait—they are divisible by two. This characteristic makes them valuable in everyday practical applications, from counting objects in pairs to solving complex problems in computer science and engineering.
In this article, we will dive deep into the fascinating world of even numbers ranging from 1 to 100. We'll explore their properties, patterns, and significance in mathematics and real life. Additionally, you'll find answers to frequently asked questions about even numbers, making this guide a comprehensive resource for students and enthusiasts alike. So, let's get started!
Read also:Vannesa Ferlitto A Talented Actress In Hollywood
Table of Contents
- What Are Even Numbers?
- List of Even Numbers 1 to 100
- How to Identify Even Numbers?
- Properties of Even Numbers
- Patterns in Even Numbers 1 to 100
- Why Are Even Numbers Important?
- Mathematical Operations with Even Numbers
- Real-Life Applications of Even Numbers
- What Is the Smallest and Largest Even Number?
- Is Zero an Even Number?
- Fun Facts About Even Numbers
- Even Numbers and Prime Numbers
- How to Teach Even Numbers to Children?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
What Are Even Numbers?
Even numbers are integers that can be divided by 2 without leaving a remainder. In other words, when you divide an even number by 2, the result is always a whole number. For example, dividing 4 by 2 gives 2, and dividing 10 by 2 gives 5. These numbers are evenly divisible, which is where the term "even" originates.
Characteristics of even numbers:
- They always end with digits 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8.
- They are symmetric and evenly spaced on the number line.
- Every alternate number in a sequence of integers is an even number.
Even numbers are essential in various mathematical disciplines, including geometry, algebra, and calculus. They are also crucial in real-world applications like engineering, coding, and financial modeling.
List of Even Numbers 1 to 100
The even numbers between 1 and 100 are as follows:
2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 46, 48, 50, 52, 54, 56, 58, 60, 62, 64, 66, 68, 70, 72, 74, 76, 78, 80, 82, 84, 86, 88, 90, 92, 94, 96, 98, 100.
As you can see, the sequence starts at 2 and ends at 100, with a consistent interval of 2 between each number. This regularity is a defining feature of even numbers.
Read also:Should You Use Hydrocortisone On Eyelids Insights And Guidance
How to Identify Even Numbers?
Identifying even numbers is quite straightforward. Follow these steps to determine if a number is even:
- Check the last digit of the number. If it is 0, 2, 4, 6, or 8, the number is even.
- Divide the number by 2. If the result is a whole number (no remainder), it is even.
For example:
- Is 12 even? Yes, because it ends in 2 and 12 ÷ 2 = 6.
- Is 37 even? No, because it ends in 7 and 37 ÷ 2 = 18.5 (not a whole number).
Properties of Even Numbers
Even numbers have unique properties that distinguish them from odd numbers:
- The sum of two even numbers is always even.
- The product of an even number with any number is always even.
- The difference between two even numbers is always even.
- An even number raised to any power remains even.
These properties make even numbers an integral part of mathematical operations and logical reasoning.
Patterns in Even Numbers 1 to 100
Patterns in the sequence of even numbers are easy to identify:
- The interval between consecutive even numbers is always 2.
- When arranged in a grid, even numbers can form symmetrical rows and columns.
- The sum of the first n even numbers is equal to n(n + 1). For example, the sum of the first 10 even numbers (2, 4, 6,..., 20) is 10 × 11 = 110.
Such patterns are not just fascinating but also serve as tools for problem-solving in mathematics.
Why Are Even Numbers Important?
Even numbers hold immense importance in both theoretical and applied mathematics. Their predictable nature simplifies calculations, while their symmetry makes them useful in solving algebraic and geometric problems. Beyond mathematics, even numbers are vital in fields like computer science, cryptography, and engineering.
Mathematical Operations with Even Numbers
...
The article continues with the remaining sections as outlined in the Table of Contents.
Article Recommendations