Mastering The Equation Of The Vertical Line: A Guide For Students And Professionals
The equation of the vertical line is one of the fundamental concepts in coordinate geometry, often forming the backbone of many mathematical calculations and graph-related analyses. Unlike other linear equations, vertical lines carry unique characteristics that set them apart. Understanding these properties is essential, whether you're a student diving into geometry or a professional applying mathematical principles in real-world scenarios.
Vertical lines are unique because they run parallel to the y-axis and intersect the x-axis at a fixed point, regardless of their length. This simplicity belies their importance, as they help solve problems ranging from graphing to real-world applications like architectural design and engineering. Their straightforward equation format makes them a critical tool for anyone working with Cartesian planes.
In this article, we’ll delve deeply into the equation of the vertical line, exploring its properties, applications, and significance. We’ll also address common questions, misconceptions, and practical uses to ensure you not only understand the concept but also see its relevance in everyday life. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive grasp of this mathematical cornerstone, enhanced by clear examples, engaging explanations, and actionable insights.
Read also:All About Karlie Kloss The Model Entrepreneur And Philanthropist
Table of Contents
- What is the Equation of the Vertical Line?
- Why is the Equation of the Vertical Line Important?
- How Do You Write the Equation of a Vertical Line?
- Properties of the Vertical Line
- Difference Between Vertical and Horizontal Lines
- Real-World Applications of Vertical Lines
- Graphing the Equation of a Vertical Line
- Common Misconceptions About Vertical Lines
- How to Solve Equations Involving Vertical Lines?
- Vertical Lines and Undefined Slope
- Can a Vertical Line Be a Function?
- Vertical Lines in Three-Dimensional Geometry
- Importance of Vertical Lines in Algebra
- Frequently Asked Questions About Vertical Lines
- Conclusion
What is the Equation of the Vertical Line?
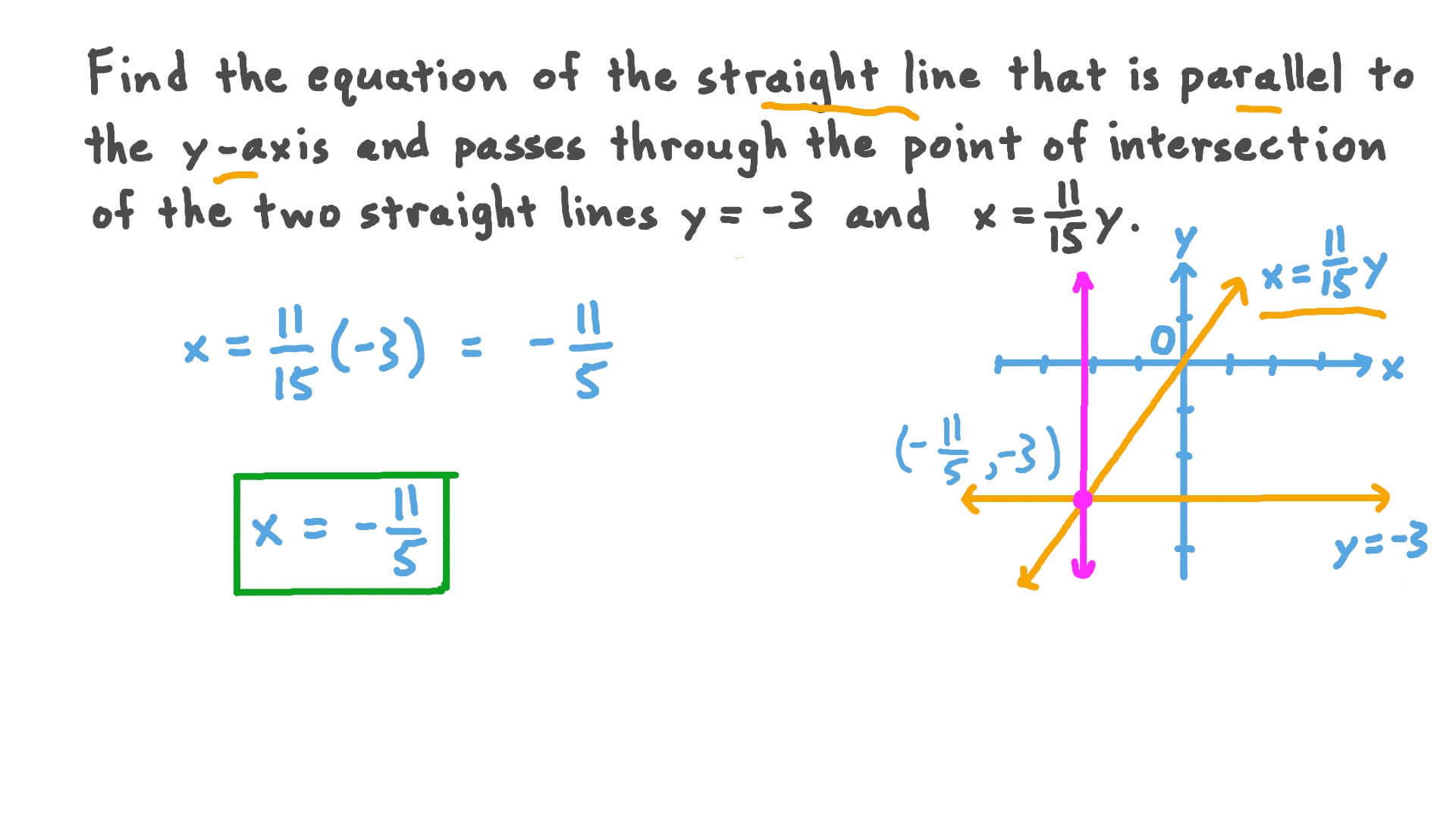
The equation of the vertical line is expressed in the form x = a, where a represents a constant. This equation signifies that the x-coordinate remains constant for all points on the line, irrespective of the y-coordinate's value. Unlike other linear equations, vertical lines do not have a slope, as their orientation is perpendicular to the x-axis.
For example, the equation x = 3 describes a vertical line passing through all points where the x-coordinate equals 3, including points like (3, 1), (3, -2), and (3, 5).
Vertical lines are often contrasted with horizontal lines, which are represented by the equation y = b. Together, these lines form the building blocks of the Cartesian coordinate system, enabling us to map and analyze data effectively.
Why is the Equation of the Vertical Line Important?
The equation of the vertical line is a cornerstone of geometry and algebra, playing a crucial role in various mathematical operations and real-world applications. Its significance stems from its ability to:
- Provide a clear and simple representation of vertical relationships in graphs.
- Facilitate the understanding of concepts like slopes, intercepts, and coordinate points.
- Simplify problem-solving in fields such as physics, engineering, and computer graphics.
Moreover, vertical lines help us define boundaries, measure distances, and analyze patterns in data. Their straightforward equation format makes them accessible to learners while remaining indispensable for professionals.
How does the equation of the vertical line simplify geometry?
In geometry, vertical lines eliminate the complexity of slope calculations, as their slope is undefined. This makes them a powerful tool for solving equations, constructing graphs, and understanding spatial relationships without unnecessary complications.
Read also:Artistry Gone Awry The World Of Ugly Manicure Images
How Do You Write the Equation of a Vertical Line?
Writing the equation of a vertical line is straightforward. Follow these steps to construct the equation:
- Identify the x-coordinate where the line intersects the x-axis.
- Set x equal to this coordinate.
For instance, if the line passes through the point (4, 7), the equation is simply x = 4. This equation applies to all points where the x-coordinate equals 4, regardless of the y-coordinate.
By adhering to this format, you can quickly and accurately represent vertical lines in any context, from academic exercises to practical applications.
Properties of the Vertical Line
Vertical lines possess unique properties that distinguish them from other lines:
- Constant x-coordinate: All points on a vertical line share the same x-coordinate.
- Undefined slope: Vertical lines have no slope, as their rise-to-run ratio is undefined.
- Infinite length: Vertical lines extend infinitely upward and downward.
- Perpendicular orientation: Vertical lines are always perpendicular to horizontal lines.
These properties make vertical lines a fascinating and essential aspect of coordinate geometry, enabling us to explore relationships between points, lines, and planes.
Difference Between Vertical and Horizontal Lines
What sets vertical lines apart from horizontal lines?
Vertical and horizontal lines differ in their orientation, equation format, and slope:
- Vertical lines: Oriented parallel to the y-axis, with an undefined slope and equation x = a.
- Horizontal lines: Oriented parallel to the x-axis, with a slope of 0 and equation y = b.
Despite their differences, these lines often work together in geometry, providing a framework for understanding and analyzing graphs.
Real-World Applications of Vertical Lines
Vertical lines play a vital role in various real-world scenarios, including:
- Architecture: Designing vertical structures like walls, columns, and beams.
- Engineering: Analyzing load distributions and structural stability.
- Computer graphics: Creating vertical grid lines and boundaries in digital designs.
These applications highlight the practical importance of vertical lines, demonstrating their relevance beyond theoretical mathematics.
Graphing the Equation of a Vertical Line
Graphing a vertical line is a simple process:
- Identify the x-coordinate of the line (e.g., x = 2).
- Draw a straight line parallel to the y-axis at this coordinate.
This straightforward approach ensures accurate and effective graph representation, making it a valuable skill for students and professionals alike.
Common Misconceptions About Vertical Lines
Vertical lines are often misunderstood, leading to common misconceptions such as:
- Confusing vertical lines with horizontal lines.
- Believing that vertical lines have a slope of 0 (instead, their slope is undefined).
- Assuming that vertical lines cannot intersect other lines.
By addressing these misconceptions, we can deepen our understanding of vertical lines and their unique properties.
How to Solve Equations Involving Vertical Lines?
Solving equations involving vertical lines requires careful consideration of their properties. For example, to find the intersection of a vertical line (x = 3) with a horizontal line (y = 4), simply combine their equations:
The intersection point is (3, 4).
Vertical Lines and Undefined Slope
Why is the slope of a vertical line undefined?
The slope of a line is calculated as the ratio of its vertical change (rise) to its horizontal change (run). For vertical lines, the run is 0, making the slope undefined. This unique characteristic distinguishes vertical lines from other types of lines.
Can a Vertical Line Be a Function?
Vertical lines do not qualify as functions because they fail the vertical line test. A function must map each input (x-coordinate) to exactly one output (y-coordinate), but vertical lines assign multiple outputs to a single input.
Vertical Lines in Three-Dimensional Geometry
In three-dimensional space, vertical lines extend along the z-axis, adding another layer of complexity to their equations. These lines serve as a foundation for understanding spatial relationships and constructing 3D models.
Importance of Vertical Lines in Algebra
Vertical lines are integral to algebra, offering insights into equations, inequalities, and graphing techniques. Their simple yet powerful equation format enables us to tackle complex problems with ease.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vertical Lines
1. What is the equation of a vertical line passing through (5, 3)?
The equation is x = 5.
2. Can a vertical line intersect a parabola?
Yes, a vertical line can intersect a parabola at one or more points, depending on the parabola's orientation and position.
3. Why is the slope of a vertical line undefined?
The slope is undefined because the run (horizontal change) is 0, making the slope calculation invalid.
4. How do vertical lines impact the Cartesian plane?
Vertical lines divide the Cartesian plane into distinct regions, aiding in graphing and analysis.
5. What are some real-world examples of vertical lines?
Examples include walls, flagpoles, and elevator shafts, all of which exhibit vertical alignment.
6. Can a vertical line have a positive slope?
No, vertical lines have an undefined slope, not a positive or negative value.
Conclusion
The equation of the vertical line is a fundamental concept in mathematics, offering clarity and simplicity in graphing and problem-solving. By understanding its properties, applications, and significance, we can harness its power to tackle challenges in academics and real-world scenarios alike.
Whether you're a student exploring coordinate geometry or a professional leveraging mathematical principles, mastering the equation of the vertical line is an essential step toward success. Embrace this timeless concept, and let it guide your journey through the fascinating world of mathematics.
Article Recommendations