RAID 0 Vs RAID 1: Which Data Storage Solution Fits Your Needs Best?
When it comes to data storage, reliability, performance, and redundancy are the key factors to consider. RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a technology that combines multiple hard drives into a single system to enhance storage capabilities. Among the many RAID configurations available, RAID 0 and RAID 1 are the most commonly used, catering to different storage needs and preferences. But how do you choose between RAID 0 and RAID 1?
RAID 0 is known for its exceptional speed and performance, achieved by striping data across multiple disks. However, it lacks redundancy, meaning if one drive fails, all data is lost. On the other hand, RAID 1 prioritizes data protection by mirroring the same data onto two drives, ensuring redundancy at the cost of reduced storage capacity. Choosing between these two RAID levels depends on your specific needs, whether it's speed or reliability.
In this article, we'll dive into a detailed comparison of RAID 0 vs RAID 1, covering everything from their functionalities, advantages, disadvantages, and use cases, to help you make an informed decision. Whether you're setting up a gaming PC, managing a server, or securing sensitive data, understanding the differences between these RAID configurations is crucial. So, let’s get started with the ultimate guide to RAID 0 vs RAID 1!
Read also:Commanders Game A Strategic Battle Experience
Table of Contents
- What is RAID?
- How Does RAID Work?
- What is RAID 0?
- What are the Advantages of RAID 0?
- What are the Disadvantages of RAID 0?
- What is RAID 1?
- What are the Advantages of RAID 1?
- What are the Disadvantages of RAID 1?
- RAID 0 vs RAID 1: Side-by-Side Comparison
- Which RAID Level is Right for You?
- Applications of RAID 0
- Applications of RAID 1
- Can You Combine RAID 0 and RAID 1?
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
What is RAID?
RAID, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks, is a storage technology that combines multiple physical drives into a single logical unit. Each RAID configuration, known as a RAID level, has specific benefits and trade-offs in terms of performance, redundancy, and capacity. RAID is commonly used in both personal and enterprise systems to achieve faster data access, increased storage capacity, and better data protection.
How Does RAID Work?
RAID works by distributing or duplicating data across multiple drives in a specific configuration. Depending on the RAID level, data can either be striped (split across drives), mirrored (copied exactly onto multiple drives), or both. This distribution reduces the risk of data loss, improves read/write speeds, or increases storage efficiency based on the chosen RAID level.
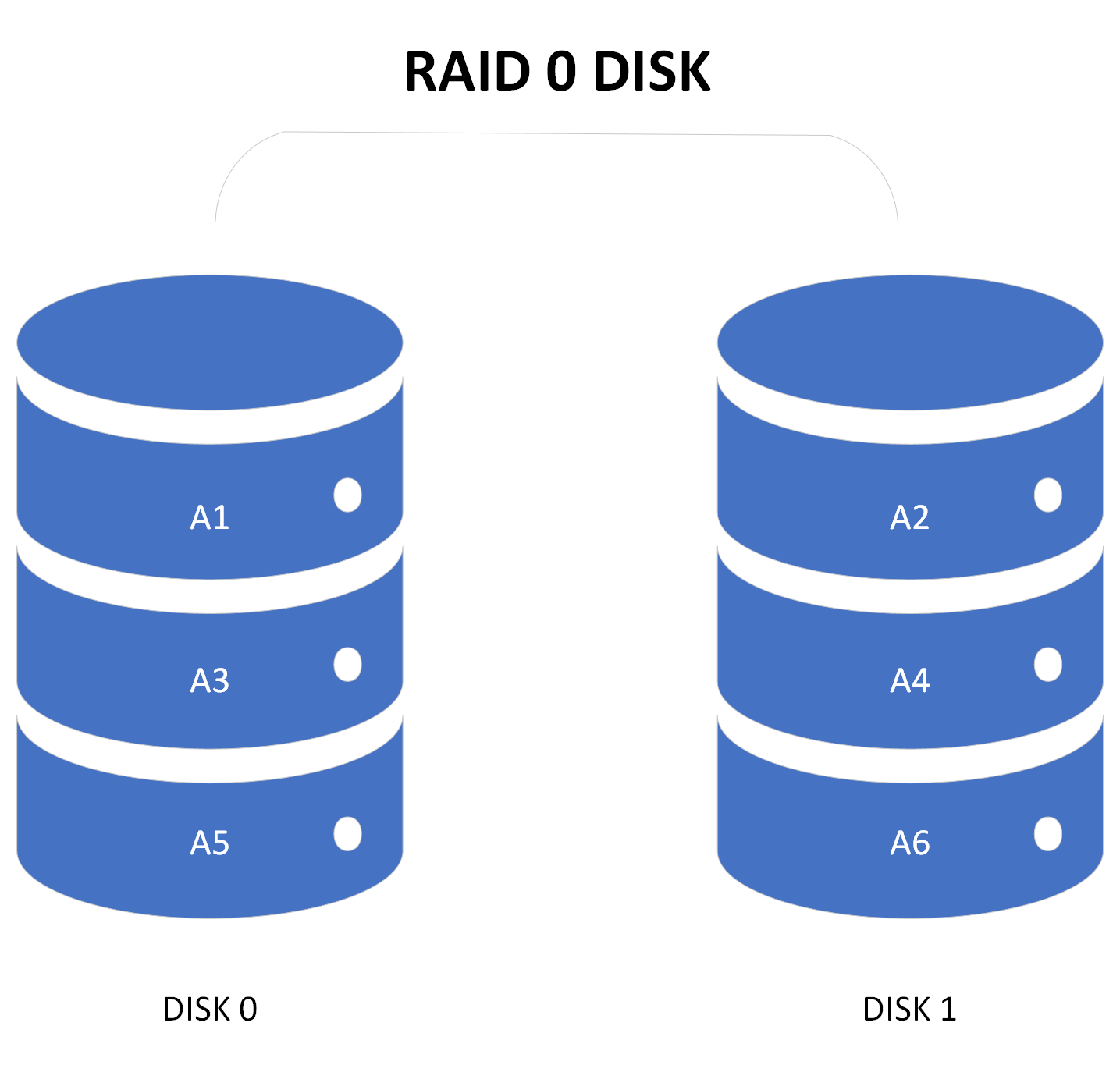
What is RAID 0?
RAID 0 is a performance-focused RAID configuration that uses a method called "striping." Data is divided into blocks and spread evenly across all drives in the array. This allows multiple drives to read and write data simultaneously, significantly improving performance. However, RAID 0 does not offer data redundancy, meaning if one drive fails, all data is lost. It is best suited for applications where speed is prioritized over reliability.
What are the Advantages of RAID 0?
- High performance for read and write operations.
- Full utilization of available storage space since no redundancy is involved.
- Ideal for gaming, video editing, and other tasks requiring fast data access.
What are the Disadvantages of RAID 0?
- No data redundancy; a single drive failure leads to total data loss.
- Not suitable for critical data storage or systems requiring high reliability.
What is RAID 1?
RAID 1 is a redundancy-focused RAID configuration that uses "mirroring." Data is duplicated onto two drives, ensuring that if one drive fails, the other contains an exact copy of the data. While RAID 1 offers excellent data protection, it comes at the cost of halving the effective storage capacity since each drive stores identical data. It is ideal for scenarios where data integrity and reliability are critical.
What are the Advantages of RAID 1?
- Provides excellent data redundancy and fault tolerance.
- Ensures data availability even in the event of a single drive failure.
- Simple setup and easy recovery process.
What are the Disadvantages of RAID 1?
- Effective storage capacity is halved due to mirroring.
- Read/write performance may not match RAID 0 for large workloads.
- Higher cost per gigabyte compared to other RAID levels.
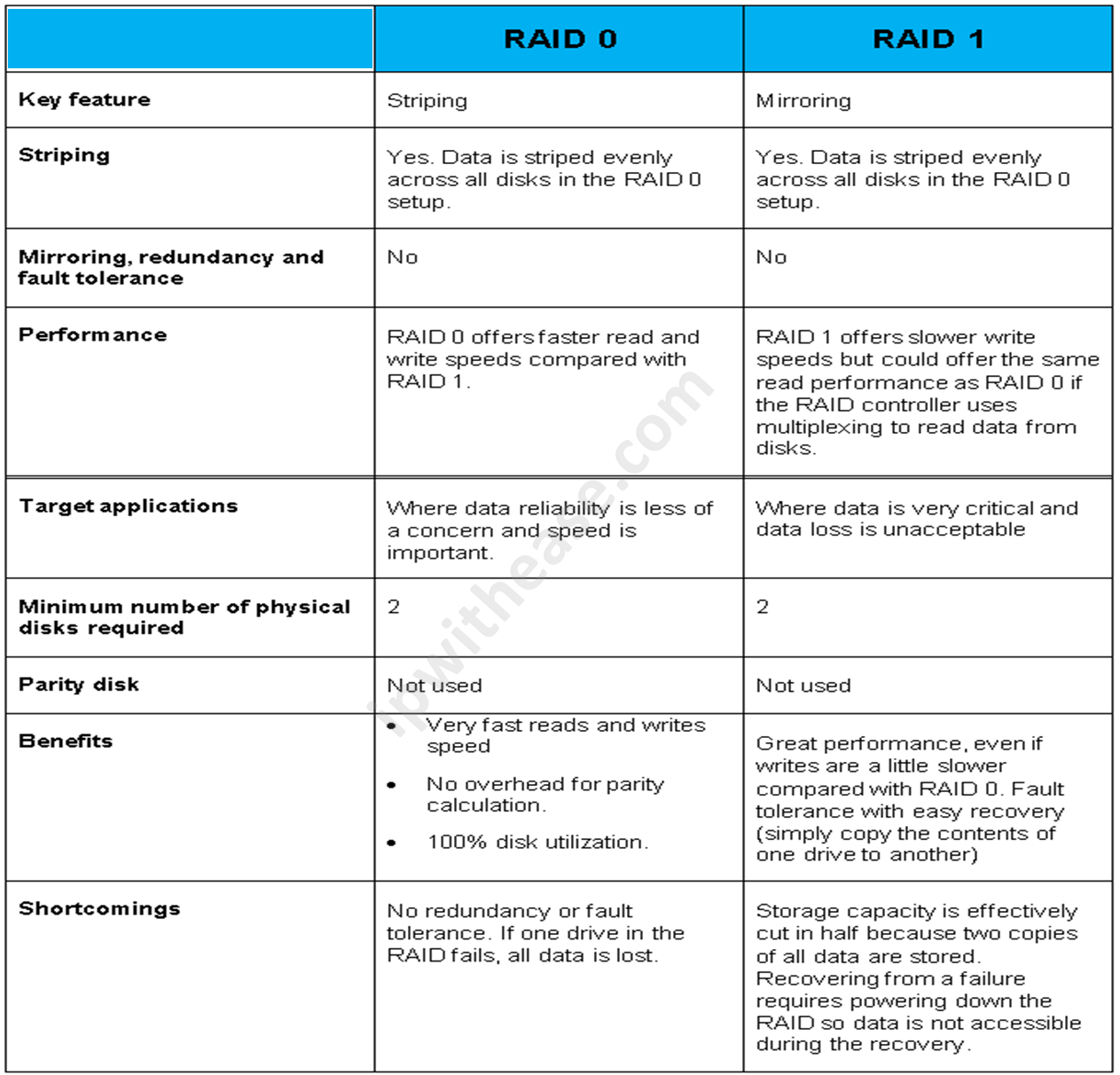
RAID 0 vs RAID 1: Side-by-Side Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison table to help you understand the key differences between RAID 0 and RAID 1:
| Feature | RAID 0 | RAID 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | High | Moderate |
| Redundancy | None | High |
| Storage Efficiency | 100% | 50% |
| Use Case | Gaming, video editing | Critical data storage |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Which RAID Level is Right for You?
The choice between RAID 0 and RAID 1 depends on your specific requirements. If you prioritize speed and performance, RAID 0 is the better option. However, if data protection and reliability are your primary concerns, RAID 1 is the way to go. Assess your needs carefully, considering factors like budget, storage capacity, and risk tolerance, to make the best decision.
Read also:Viviana Serna A Star In The Making Biography Career And More
Applications of RAID 0
RAID 0 is commonly used in scenarios where performance is critical, such as:
- Gaming setups for faster load times.
- Video editing and rendering tasks.
- High-speed data processing applications.
Applications of RAID 1
RAID 1 is ideal for situations requiring high data reliability, such as:
- Storing sensitive or critical data.
- Enterprise systems requiring fault tolerance.
- Personal backups and archiving.
Can You Combine RAID 0 and RAID 1?
Yes, combining RAID 0 and RAID 1 is possible through nested RAID levels like RAID 10. This configuration combines the performance benefits of RAID 0 with the redundancy of RAID 1. However, it requires a minimum of four drives and comes with higher costs and complexity, making it suitable for advanced users or enterprise environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is RAID 0 faster than RAID 1?
Yes, RAID 0 is faster than RAID 1 because it uses striping to distribute data across multiple drives, allowing for simultaneous read/write operations. RAID 1, on the other hand, focuses on redundancy rather than speed.
2. Can I use RAID 0 for critical data?
RAID 0 is not recommended for critical data because it lacks redundancy. If one drive fails, all data is lost. Consider RAID 1 or a higher RAID level for storing important information.
3. How many drives do I need for RAID 1?
You need at least two drives for RAID 1, as it involves mirroring data onto both drives for redundancy.
4. What happens if a drive fails in RAID 1?
If a drive fails in RAID 1, the system continues to operate using the mirrored copy on the remaining drive. You can replace the failed drive without losing data.
5. Is RAID 10 better than RAID 0 or RAID 1?
RAID 10 combines the benefits of RAID 0 and RAID 1, offering both performance and redundancy. However, it requires a minimum of four drives and is more expensive.
6. Can I switch from RAID 0 to RAID 1 without losing data?
No, switching from RAID 0 to RAID 1 requires reformatting the drives, which will erase all data. Ensure you back up your data before making such changes.
Conclusion
Choosing between RAID 0 and RAID 1 boils down to understanding your specific needs. RAID 0 offers unmatched performance but sacrifices data redundancy, making it ideal for tasks like gaming and video editing. RAID 1, on the other hand, provides robust data protection, making it the go-to choice for critical data storage. By carefully evaluating your requirements and considering the pros and cons of each RAID level, you can select the storage solution that best aligns with your goals.
Whether you're a gamer, a content creator, or a business owner, the right RAID configuration can significantly enhance your storage experience. Always remember to prioritize backups and consider combining RAID levels like RAID 10 for the perfect balance of performance and redundancy.
Article Recommendations