All About Pneumonia Kinds: Comprehensive Guide For Better Understanding
Pneumonia is a complex and potentially life-threatening condition that affects millions of people worldwide each year. It is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs, leading to symptoms such as cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. The severity of pneumonia can range from mild to severe, and understanding the various kinds of pneumonia is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment.
There are several kinds of pneumonia, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and treatment protocols. These include bacterial, viral, fungal, and aspiration pneumonia, among others. Each type necessitates a different approach to treatment and recovery, making it essential for healthcare providers and patients alike to be informed about the specific characteristics of each kind. This knowledge can significantly impact the management and prognosis of the condition.
In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the various kinds of pneumonia, discussing their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. We will also explore preventive measures and provide insights into how lifestyle choices and pre-existing health conditions can influence the risk of developing pneumonia. By the end of this article, you will have a thorough understanding of pneumonia kinds, helping you make informed decisions about your health or the health of those you care for.
Read also:Amica Insurance A Trusted Name In The World Of Insurance
Table of Contents
- What Causes Pneumonia?
- Bacterial Pneumonia
- Viral Pneumonia
- Fungal Pneumonia
- Aspiration Pneumonia
- Symptoms of Pneumonia
- How is Pneumonia Diagnosed?
- Treatment Options for Pneumonia
- Preventing Pneumonia
- Risk Factors of Pneumonia
- Recovery from Pneumonia
- How Can Lifestyle Influence Pneumonia Risk?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What Causes Pneumonia?
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of pathogens including bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Each pathogen type results in different kinds of pneumonia, necessitating unique treatment approaches. Understanding these causes is foundational in diagnosing and managing pneumonia effectively.
Bacterial Pathogens
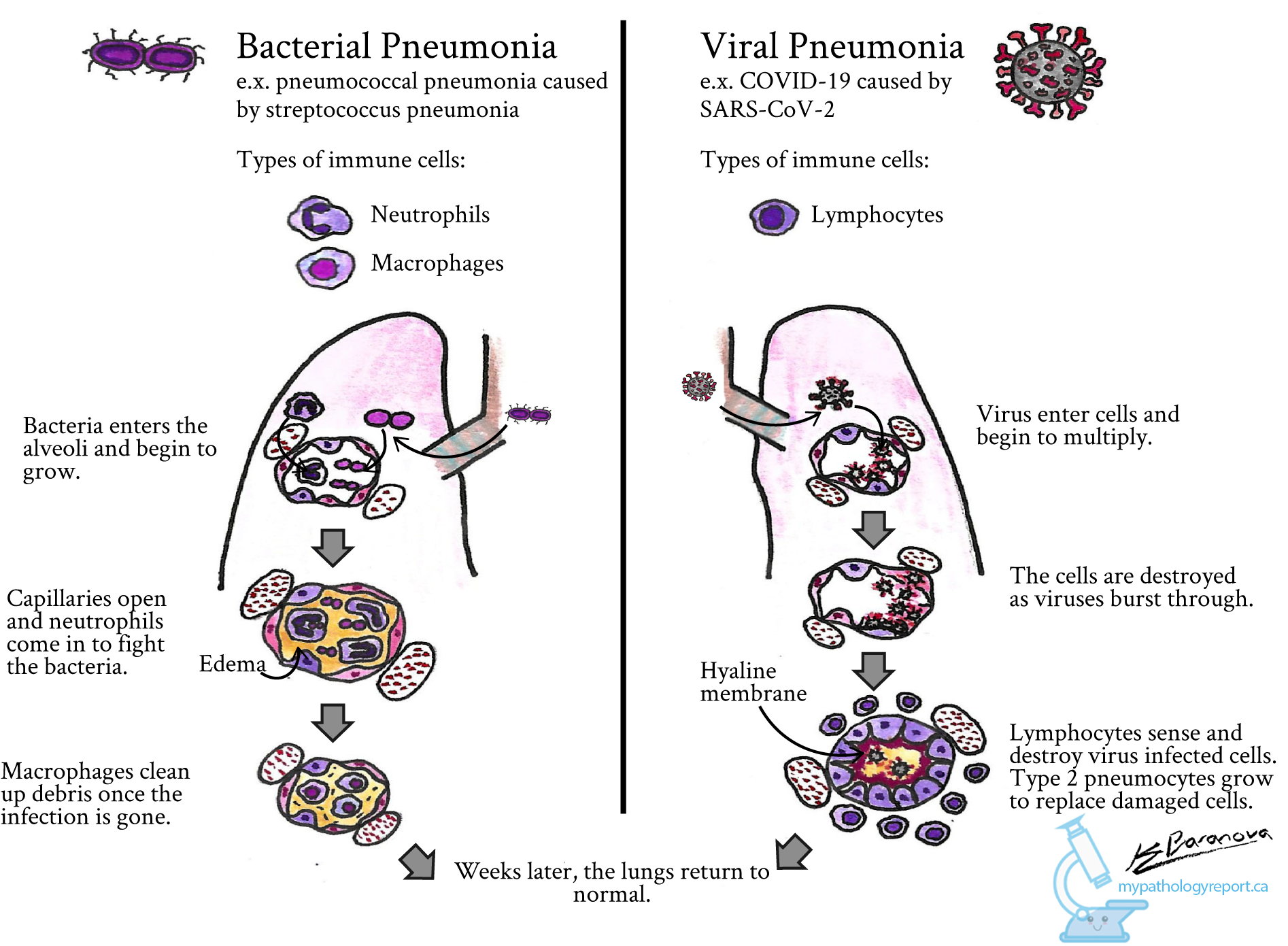
Bacterial pneumonia is often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae, but other bacteria such as Haemophilus influenzae and Legionella pneumophila can also be culprits. Bacterial pneumonia typically follows a viral respiratory infection that weakens the immune system, making it easier for bacteria to invade the lungs.
Viral Pathogens
Viruses, such as influenza, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and the novel coronavirus (COVID-19), are common causes of viral pneumonia. These viruses can lead to inflammation in the lungs and are particularly dangerous in individuals with weakened immune systems.
Fungal Pathogens
Fungal pneumonia is less common and usually affects people with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS or undergoing chemotherapy. Common fungi causing pneumonia include Histoplasma, Coccidioides, and Cryptococcus.
Bacterial Pneumonia
Bacterial pneumonia is a severe type of pneumonia that requires prompt medical attention. It often develops suddenly, starting with a high fever and shaking chills. Bacterial pneumonia can affect people of all ages, but it is more prevalent in older adults, young children, and individuals with chronic health conditions.
Symptoms of Bacterial Pneumonia
Common symptoms of bacterial pneumonia include:
Read also:Effective Solutions To Deal With A Large Zit On Face
- High fever
- Chills
- Cough with green or yellow mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
Treatment
The treatment for bacterial pneumonia usually involves antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria causing the infection. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary, especially if the patient experiences severe symptoms or has underlying health issues.
Viral Pneumonia
Viral pneumonia is caused by various viruses, including influenza and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). It can also be a complication of viral infections like COVID-19. While viral pneumonia is generally less severe than bacterial pneumonia, it can still be life-threatening, particularly for at-risk populations.
Symptoms of Viral Pneumonia
Symptoms can include:
- Fever
- Dry cough
- Headache
- Muscle pain
- Fatigue
Treatment
Treatment for viral pneumonia primarily involves supportive care, such as rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms. Antiviral medications may be prescribed in certain cases, particularly for influenza-related pneumonia.
Fungal Pneumonia
Fungal pneumonia is less common and usually occurs in people with weakened immune systems. This kind of pneumonia is caused by fungi found in soil or bird droppings, which are inhaled into the lungs.
Symptoms of Fungal Pneumonia
Symptoms may include:
- Cough
- Fever
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
Treatment
Treatment for fungal pneumonia typically involves antifungal medications. The type of antifungal prescribed depends on the specific fungus causing the infection. Treatment duration can be lengthy, often several weeks to months, depending on the severity of the infection.
Aspiration Pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia occurs when food, liquid, or vomit is inhaled into the lungs, leading to infection. This type is more common in people with swallowing difficulties or neurological disorders that affect the swallowing reflex.
Symptoms of Aspiration Pneumonia
Symptoms may include:
- Cough with putrid or foul-smelling sputum
- Difficulty swallowing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
Treatment
Treatment often involves antibiotics to address the infection, along with supportive care to manage symptoms. In some cases, interventions to improve swallowing function may be recommended to prevent recurrence.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include cough, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. It's important to note that symptoms can be more severe in certain populations, such as the elderly, infants, and individuals with compromised immune systems.
Common Symptoms
- Cough, which may produce phlegm
- Fever, sweating, and chills
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Fatigue
Severe Symptoms
In severe cases, pneumonia can cause symptoms such as:
- Confusion, especially in older adults
- Lower than normal body temperature
- Nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea
How is Pneumonia Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of pneumonia typically involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic tests. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and recovery.
Physical Examination
During a physical exam, a healthcare provider will listen to the lungs with a stethoscope to detect abnormal sounds, such as crackling or wheezing, which may indicate pneumonia.
Diagnostic Tests
- Chest X-ray: This is the most common test used to diagnose pneumonia and determine the extent of infection in the lungs.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help confirm the infection and identify the causative pathogen.
- Sputum Test: Analyzing the sputum can provide information on the type of pathogen causing the infection.
Treatment Options for Pneumonia
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the type and severity of the infection. Early and appropriate treatment is essential to prevent complications and ensure a full recovery.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for bacterial pneumonia. The choice of antibiotic depends on the type of bacteria involved, patient age, and overall health status.
Antiviral Medications
In cases of viral pneumonia, antiviral medications may be prescribed, particularly for influenza-related pneumonia. These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms.
Supportive Care
Supportive care includes rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms such as fever and cough. In severe cases, hospitalization may be necessary to provide oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation.
Preventing Pneumonia
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing pneumonia. Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent pneumonia caused by certain bacteria and viruses.
Vaccination
- Pneumococcal Vaccine: This vaccine protects against Streptococcus pneumoniae, a common cause of bacterial pneumonia.
- Influenza Vaccine: The flu vaccine can help prevent influenza-related pneumonia.
Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can strengthen the immune system and reduce the risk of pneumonia. This includes eating a balanced diet, getting regular exercise, avoiding smoking, and practicing good hygiene.
Risk Factors of Pneumonia
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing pneumonia, making it important to be aware of these risks and take appropriate precautions.
Age
Young children and older adults are at a higher risk of pneumonia due to less robust immune systems.
Chronic Health Conditions
Individuals with chronic health conditions, such as asthma, diabetes, and heart disease, are more susceptible to pneumonia.
Weakened Immune System
People with weakened immune systems, due to conditions like HIV/AIDS or cancer treatment, are at increased risk for pneumonia.
Recovery from Pneumonia
Recovery from pneumonia can take time, depending on the type and severity of the infection and the patient's overall health. It's essential to follow medical advice and complete any prescribed treatments to ensure a full recovery.
Rest and Recovery
Adequate rest is crucial for recovery. Patients should avoid strenuous activities and ensure they get enough sleep to help the body heal.
Follow-up Care
Regular follow-up with a healthcare provider is important to monitor recovery and address any complications that may arise.
How Can Lifestyle Influence Pneumonia Risk?
Lifestyle choices play a significant role in influencing the risk of developing pneumonia. Making healthy lifestyle choices can bolster the immune system and reduce susceptibility to infections.
Diet and Nutrition
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can provide essential nutrients that support immune function and reduce the risk of pneumonia.
Exercise
Regular physical activity can enhance lung function and overall health, decreasing the likelihood of respiratory infections like pneumonia.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main kinds of pneumonia?
The main kinds of pneumonia include bacterial, viral, fungal, and aspiration pneumonia, each with distinct causes and treatment protocols.
Can pneumonia be contagious?
Yes, pneumonia can be contagious, particularly viral and bacterial kinds, which can spread through respiratory droplets from coughing or sneezing.
How long does it take to recover from pneumonia?
Recovery time varies but generally ranges from a few weeks to several months, depending on the severity and type of pneumonia.
Is it possible to have pneumonia without a fever?
Yes, particularly in older adults and individuals with weakened immune systems, pneumonia can occur without a noticeable fever.
Can pneumonia recur?
Yes, pneumonia can recur, especially in individuals with chronic health issues or weakened immune systems. Preventive measures can help reduce recurrence.
What is walking pneumonia?
Walking pneumonia is a milder form of pneumonia, often caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and typically does not require hospitalization.
Conclusion
Understanding the different kinds of pneumonia is vital for effective prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. By recognizing the symptoms and risk factors associated with each type, individuals can take appropriate measures to protect themselves and seek timely medical intervention when necessary. Through vaccination, healthy lifestyle choices, and awareness of risk factors, the impact of pneumonia can be significantly reduced, improving outcomes and quality of life for those affected.
Article Recommendations