Psoriasis Skin: Navigating The Challenges And Solutions
Psoriasis skin is a complex and often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This chronic skin disorder is characterized by red, scaly patches that can appear anywhere on the body. While it is not contagious, the visible symptoms can lead to significant social and psychological impacts. Understanding the intricacies of psoriasis skin is crucial for those affected, as well as for their loved ones and caregivers. This article delves into the nature of psoriasis skin, exploring its causes, symptoms, and the latest treatment options available.
Living with psoriasis skin can be challenging, as flare-ups can be unpredictable and often painful. The condition is influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, making it unique to each individual. Despite the challenges, there is hope. With advancements in medical research, new treatments are continually being developed to manage symptoms more effectively. This has led to improved quality of life for many sufferers, allowing them to manage the condition with greater ease.
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and holistic approaches can also play a significant role in managing psoriasis skin. Diet, stress management, and skincare routines can all impact the severity and frequency of flare-ups. By taking a comprehensive approach to treatment, individuals with psoriasis skin can find a path to relief and a more comfortable life. This article provides a detailed overview of these strategies, along with practical tips and insights to empower those living with this condition.
Read also:Stefanie Martini Rising Star Of British Television And Film
Table of Contents
- What is Psoriasis Skin?
- What Causes Psoriasis Skin?
- Common Symptoms of Psoriasis Skin
- Different Types of Psoriasis Skin
- How is Psoriasis Skin Diagnosed?
- Conventional Treatment Options for Psoriasis Skin
- Emerging Treatments and Research
- Holistic and Lifestyle Approaches
- Impact of Diet on Psoriasis Skin
- Managing Stress and Mental Health
- Skincare Routines for Psoriasis Skin
- Support Networks and Communities
- Living with Psoriasis Skin
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
What is Psoriasis Skin?
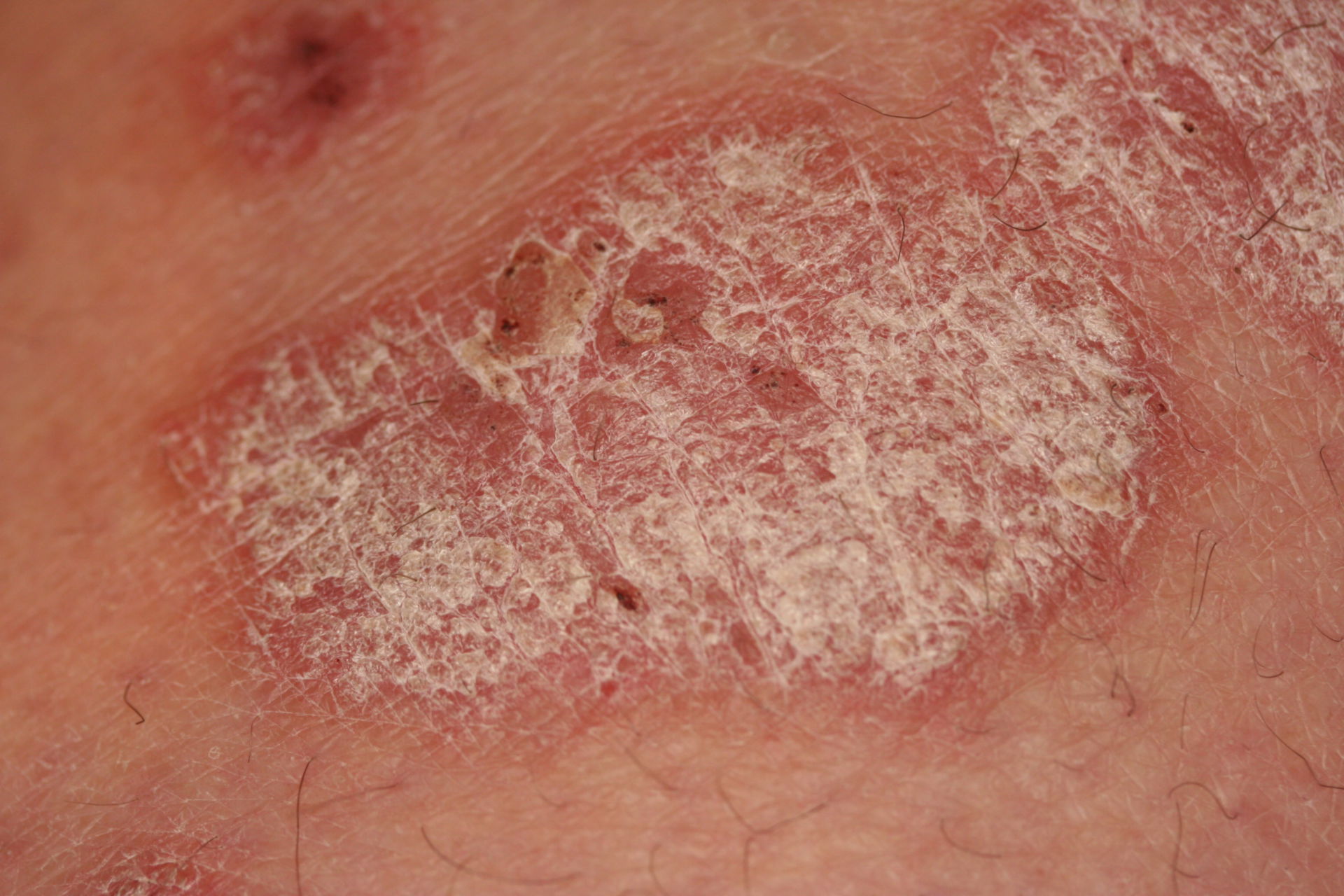
Psoriasis skin is a chronic autoimmune condition that primarily affects the skin. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, causing them to multiply rapidly. This abnormal growth leads to the formation of thick, red patches with silvery scales, which are often itchy and painful. Psoriasis skin can vary in severity, from small localized patches to full-body coverage.
While the exact cause of psoriasis skin remains unknown, it is believed to be related to genetic and environmental factors. The condition can develop at any age, but it is most commonly diagnosed in adults. Psoriasis skin is not contagious, meaning it cannot be spread through physical contact.
There are several different types of psoriasis skin, each with its own set of characteristics and symptoms. These include plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis. Each type presents unique challenges and requires a tailored approach to treatment.
What Causes Psoriasis Skin?
The causes of psoriasis skin are complex and involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Research suggests that certain genes may predispose individuals to develop psoriasis skin. If a person has a family history of the condition, their risk of developing it increases significantly.
Environmental triggers can also play a significant role in the onset and exacerbation of psoriasis skin. Common triggers include:
- Stress
- Infections, such as strep throat
- Skin injuries, like cuts or sunburns
- Certain medications, including lithium and beta-blockers
- Weather, particularly cold and dry climates
Understanding these triggers can help individuals manage their condition more effectively by avoiding or minimizing exposure to known triggers.
Read also:Avant Singer A Revolutionary Voice In Modern Music
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis Skin
The symptoms of psoriasis skin can vary widely among individuals, depending on the type and severity of the condition. However, some common symptoms include:
- Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
- Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
- Itching, burning, or soreness
- Thickened or pitted nails
- Swollen and stiff joints
The location and severity of these symptoms can fluctuate, with some individuals experiencing only mild irritation, while others may have severe, widespread patches that significantly impact their quality of life. Symptoms can also go through cycles, with periods of flare-ups followed by times of remission.
Different Types of Psoriasis Skin
Psoriasis skin can manifest in several different forms, each with its own distinct characteristics. The most common types include:
- Plaque Psoriasis: The most prevalent form, characterized by raised, red patches covered with a silvery-white buildup of dead skin cells. These patches are often itchy and painful.
- Guttate Psoriasis: Often starts in childhood or young adulthood, presenting as small, dot-like lesions. It can be triggered by a strep infection.
- Inverse Psoriasis: Occurs in skin folds, such as under the breasts or in the groin area. It appears as bright red, shiny lesions and is often aggravated by friction and sweating.
- Pustular Psoriasis: Characterized by white pustules (blisters of non-infectious pus) surrounded by red skin. It can occur on any part of the body, but is most common on the hands and feet.
- Erythrodermic Psoriasis: A severe form that leads to widespread redness over large areas of the body. This type can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Each type of psoriasis skin requires a specific approach to treatment, emphasizing the importance of an accurate diagnosis by a healthcare professional.
How is Psoriasis Skin Diagnosed?
Diagnosing psoriasis skin typically involves a physical examination by a dermatologist. The characteristic appearance of the skin lesions is often sufficient for diagnosis. However, in some cases, a skin biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin disorders.
The dermatologist will also take into consideration the patient's medical history and any family history of psoriasis or other autoimmune diseases. This information helps in understanding potential genetic predispositions and identifying possible triggers.
There are no specific blood tests for diagnosing psoriasis skin, but tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions or to assess the overall health of the patient. Once diagnosed, the severity of the condition will be assessed to guide treatment decisions.
Conventional Treatment Options for Psoriasis Skin
Treatment for psoriasis skin aims to reduce inflammation, clear the skin, and manage symptoms. The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the condition and the response to previous treatments. Conventional treatment options include:
- Topical Treatments: These are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis skin. They include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids, which help to reduce inflammation and slow down the growth of skin cells.
- Phototherapy: Also known as light therapy, this treatment involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. It is effective for moderate to severe cases of psoriasis skin.
- Systemic Medications: For severe psoriasis skin, oral or injected medications may be prescribed. These include methotrexate, cyclosporine, and biologics, which work by targeting the immune system to reduce inflammation.
It is important for patients to work closely with their healthcare provider to find the most effective and appropriate treatment plan for their specific needs.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Research in the field of psoriasis skin is ongoing, with new treatments and therapies continually being developed. Recent advances include:
- Biologic Drugs: These are newer medications that target specific parts of the immune system. They have shown promise in treating moderate to severe psoriasis skin with fewer side effects than traditional systemic medications.
- Janus Kinase (JAK) Inhibitors: These oral medications work by blocking certain enzymes involved in the immune response. They offer a new option for patients who do not respond to other treatments.
- Gene Therapy: Research is being conducted to explore the potential of gene therapy in treating psoriasis skin by directly targeting the genetic factors involved in the condition.
These emerging treatments offer hope for more effective management of psoriasis skin, with the potential for fewer side effects and improved outcomes.
Holistic and Lifestyle Approaches
In addition to medical treatments, holistic and lifestyle approaches can play a significant role in managing psoriasis skin. These strategies focus on overall health and well-being, aiming to reduce the severity and frequency of flare-ups. Key approaches include:
- Dietary Changes: Certain foods may trigger or exacerbate psoriasis skin. A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, like fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can help manage symptoms.
- Stress Management: Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis skin flare-ups. Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help reduce stress levels.
- Skincare Routine: Keeping the skin moisturized and avoiding harsh products can prevent irritation and help manage symptoms.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall health and reduce stress, which may help manage psoriasis skin.
By incorporating these lifestyle changes, individuals with psoriasis skin can improve their quality of life and better manage their condition.
Impact of Diet on Psoriasis Skin
Diet plays a crucial role in managing psoriasis skin, as certain foods can trigger or exacerbate symptoms. While there is no one-size-fits-all diet for psoriasis, some dietary changes may help reduce inflammation and improve skin health. Key dietary considerations include:
- Anti-inflammatory Foods: Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts, can help reduce inflammation. Fruits and vegetables, particularly those high in antioxidants, can also support skin health.
- Avoiding Triggers: Some individuals find that certain foods, such as gluten, dairy, and processed foods, can trigger flare-ups. Keeping a food diary can help identify personal triggers.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity is a known risk factor for psoriasis skin, and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the severity of symptoms.
Consulting with a healthcare professional or nutritionist can help individuals develop a personalized diet plan that supports their overall health and psoriasis management.
Managing Stress and Mental Health
Stress is a well-known trigger for psoriasis skin flare-ups, and managing stress is an important aspect of treatment. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, potentially leading to more frequent and severe flare-ups. Strategies for managing stress and improving mental health include:
- Meditation and Mindfulness: These practices can help individuals focus on the present moment, reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity releases endorphins, which can improve mood and reduce stress.
- Support Networks: Connecting with others who have psoriasis skin can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Professional Counseling: Therapy or counseling can help individuals develop coping strategies for managing stress and improving mental health.
By incorporating these stress management techniques, individuals with psoriasis skin can improve their overall well-being and reduce the impact of stress on their condition.
Skincare Routines for Psoriasis Skin
Developing a skincare routine tailored to psoriasis skin can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. Key components of a psoriasis-friendly skincare routine include:
- Moisturizing: Keeping the skin well-hydrated is essential to prevent dryness and cracking. Thick, fragrance-free creams or ointments are recommended.
- Gentle Cleansing: Using mild, fragrance-free cleansers can help avoid irritation. It's important to avoid scrubbing the skin, as this can exacerbate symptoms.
- Bathing Practices: Warm (not hot) baths with Epsom salts or oatmeal can soothe the skin. Limiting bath time to 15 minutes can prevent further drying of the skin.
- Sun Protection: UV exposure can help some individuals with psoriasis skin, but it's important to protect the skin from sunburn with sunscreen.
Consulting with a dermatologist can provide additional guidance on creating a skincare routine that addresses individual needs and concerns.
Support Networks and Communities
Living with psoriasis skin can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Support networks and communities can provide valuable resources and a sense of belonging for those affected by the condition. Benefits of joining a support group include:
- Emotional Support: Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with psoriasis skin can provide comfort and reassurance.
- Shared Experiences: Sharing experiences and tips with others can provide practical advice and new perspectives on managing the condition.
- Access to Resources: Support groups often provide access to educational materials, expert speakers, and information on the latest treatments and research.
Many organizations, such as the National Psoriasis Foundation, offer online and in-person support groups for individuals with psoriasis skin and their families.
Living with Psoriasis Skin
Living with psoriasis skin can present unique challenges, but with the right strategies and support, individuals can lead fulfilling lives. Key aspects of managing the condition include:
- Adhering to Treatment Plans: Consistently following prescribed treatments and working closely with healthcare providers can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
- Identifying Triggers: Keeping a journal to track potential triggers, such as stress, diet, and weather changes, can help individuals avoid or minimize exposure.
- Building a Support System: Surrounding oneself with supportive friends, family, and healthcare professionals can provide encouragement and assistance.
- Fostering a Positive Mindset: Focusing on the positive aspects of life and maintaining a hopeful attitude can improve mental health and overall well-being.
By taking a proactive approach to managing psoriasis skin, individuals can reduce the impact of the condition on their lives and achieve a greater sense of control and well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can psoriasis skin be cured?
Currently, there is no cure for psoriasis skin, but many treatment options are available to manage symptoms effectively. Patients can work with their healthcare providers to find a treatment plan that works best for them.
2. Is psoriasis skin contagious?
No, psoriasis skin is not contagious. It cannot be spread through physical contact with someone who has the condition.
3. Can diet affect psoriasis skin?
Yes, diet can play a role in managing psoriasis skin. Some individuals find that certain foods trigger flare-ups, while an anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce symptoms.
4. Does stress affect psoriasis skin?
Yes, stress is a known trigger for psoriasis skin flare-ups. Managing stress through relaxation techniques and a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the frequency and severity of symptoms.
5. Are there natural remedies for psoriasis skin?
While natural remedies cannot cure psoriasis skin, certain approaches, such as moisturizing, dietary changes, and stress management, can complement medical treatments and help manage symptoms.
6. How can I find support for living with psoriasis skin?
Many organizations, such as the National Psoriasis Foundation, offer support groups and resources for individuals with psoriasis skin. Joining a support network can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Conclusion
Psoriasis skin is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to management. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition and improve their quality of life. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment, there is hope for those living with psoriasis skin. Through a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and support networks, individuals can find relief and lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by this chronic condition.
Article Recommendations