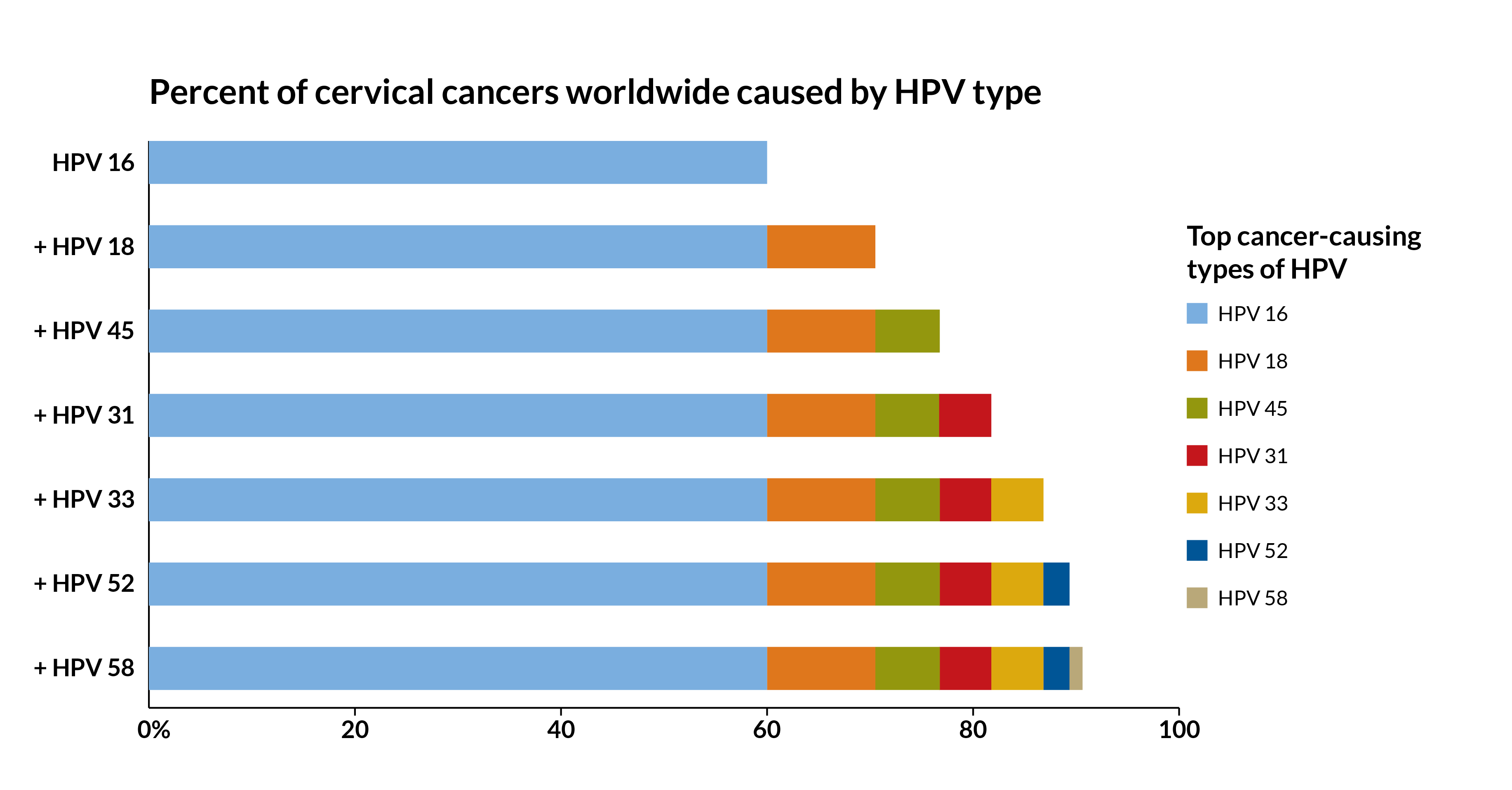HPV Wart Types: A Detailed Guide To Understanding And Managing
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. Among its many manifestations, warts are one of the most recognizable and prevalent forms. Understanding the various types of warts caused by HPV, their characteristics, and how they can be managed is crucial for anyone looking to maintain good skin health and prevent the spread of the virus. As a pervasive condition, HPV warts can appear on different parts of the body, each with its own set of challenges and treatment options.
Although warts are generally harmless, they can cause discomfort, embarrassment, and frustration for those affected. These growths vary in appearance and location, ranging from the common warts often seen on hands and fingers to plantar warts found on the soles of the feet. Beyond these, there are also flat warts, filiform warts, and genital warts, each associated with specific HPV strains. It's important to note that while warts can be contagious, they are usually treatable with a variety of medical and home remedies.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the different types of HPV warts, their symptoms, causes, and available treatments. We will also address common questions and misconceptions, providing a well-rounded understanding of this condition. Whether you're seeking information for personal reasons or to help someone else, this article will equip you with the knowledge needed to navigate the world of HPV warts confidently.
Read also:Meet Hannah Uwu A Rising Star In The Digital World
Table of Contents
- What Are HPV Warts?
- Common Warts: The Most Recognizable Type
- Plantar Warts: A Painful Foot Problem
- Flat Warts: The Subtle Skin Blemish
- Filiform Warts: The Facial Challenge
- Genital Warts: A Sensitive Issue
- How Do HPV Warts Spread?
- Diagnosis of HPV Warts: What to Expect
- Treatment Options for HPV Warts
- Can HPV Warts Be Prevented?
- Are There Any Home Remedies for HPV Warts?
- When Should I See a Doctor?
- Lifestyle and Dietary Changes to Manage HPV Warts
- Impact of HPV Warts on Mental Health
- FAQs
- Conclusion
What Are HPV Warts?
HPV warts are benign skin growths caused by the human papillomavirus. This virus has over 100 different strains, each responsible for various types of warts. The virus infects the top layer of skin, often through small cuts or abrasions, leading to the growth of warts. While these growths are typically non-cancerous, they can be unsightly and sometimes painful.
There are several types of HPV warts, each associated with specific strains of the virus. Common warts (verruca vulgaris) usually appear on the hands and fingers, while plantar warts affect the soles of the feet. Flat warts are smaller and smoother, often occurring on the face or legs. Filiform warts have a distinct, thread-like appearance, commonly found on the face, especially around the lips and eyelids. Lastly, genital warts are sexually transmitted and appear in the genital area. Understanding the specific type of wart is essential for effective treatment and management.
HPV warts are contagious and can spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching surfaces contaminated with the virus. The spread is more likely in warm, moist environments, which is why warts are common in public swimming pools or locker rooms. It's important to practice good hygiene and take precautions to prevent the transmission of the virus.
Common Warts: The Most Recognizable Type
Common warts, known scientifically as verruca vulgaris, are one of the most prevalent types of warts caused by HPV. They are characterized by their rough, raised appearance and can vary in color from white to tan or even dark brown. These warts typically appear on the hands, fingers, elbows, and knees, areas that are frequently exposed to minor trauma or abrasions.
Common warts are caused by specific strains of HPV, particularly types 2 and 4. These strains are highly contagious and can be transmitted through direct skin-to-skin contact or by touching objects that have come into contact with the wart. Although common warts are generally harmless, they can be a source of discomfort and self-consciousness, especially when they appear in visible areas.
Treatment options for common warts include over-the-counter topical treatments containing salicylic acid, which works by softening the wart and gradually removing the layers of infected skin. Cryotherapy, or freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, is another effective treatment administered by healthcare professionals. For persistent cases, laser therapy or minor surgical procedures may be considered.
Read also:Slots Of Vegas A Winning Experience Awaits You
Plantar Warts: A Painful Foot Problem
Plantar warts are a specific type of wart that develops on the soles of the feet. Unlike common warts, plantar warts grow inward due to the pressure exerted on them while walking or standing. This can cause significant discomfort and even pain, making it difficult to walk or engage in physical activities.
These warts are caused by HPV strains 1, 2, 4, 60, and 63, which thrive in warm, moist environments. As such, plantar warts are commonly contracted in communal areas such as swimming pools, gym showers, and locker rooms. They often appear as small, fleshy lesions with a rough texture and may have tiny black dots on their surface, which are clotted blood vessels.
Treatment for plantar warts may involve over-the-counter salicylic acid preparations, which help to break down the wart tissue over time. Healthcare providers might recommend cryotherapy, laser treatment, or even surgical removal for more stubborn warts. It's crucial to keep the feet clean and dry, and wearing protective footwear in public areas can help prevent the spread of the virus.
Flat Warts: The Subtle Skin Blemish
Flat warts, also known as verruca plana, are small, smooth growths that tend to appear in clusters. They are less noticeable than other types of warts due to their flat shape and can be skin-colored, pink, or slightly brown. Commonly found on the face, neck, hands, wrists, and knees, flat warts can be more prevalent in children and young adults.
These warts are caused by HPV types 3, 10, 28, and 49. They can spread easily through direct contact or by touching objects like towels or razors that have been used by an infected person. Flat warts can be particularly bothersome due to their tendency to appear in large numbers, sometimes making treatment more challenging.
Treatment options for flat warts include topical retinoids, which help to peel away the layers of the warts over time. Chemical peels and cryotherapy are also effective in reducing their appearance. Maintaining good hygiene and avoiding the sharing of personal items can help minimize the spread of flat warts.
Filiform Warts: The Facial Challenge
Filiform warts are characterized by their long, narrow, and protruding shape, resembling tiny threads or fingers. They commonly appear on the face, especially around the eyes, nose, and mouth, making them particularly noticeable. These warts can be flesh-colored or slightly darker and are caused by HPV types 1, 2, 4, 27, and 29.
Due to their location and appearance, filiform warts can cause distress and embarrassment. They are often spread through direct contact with an infected person or by touching areas of the face after coming into contact with the virus. The thin, elongated shape of filiform warts makes them relatively easy to identify.
Treatment of filiform warts typically involves professional removal methods such as cryotherapy, laser treatment, or surgical excision, to minimize scarring and potential infection. Home remedies are generally not recommended for facial warts due to the sensitive nature of the skin in this area. It's important to consult with a healthcare provider for appropriate treatment options.
Genital Warts: A Sensitive Issue
Genital warts are a type of sexually transmitted infection caused by certain strains of HPV, most commonly types 6 and 11. These warts appear in the genital area, including the vulva, vagina, cervix, penis, scrotum, or anus. They can vary in size and appearance, from small, flesh-colored bumps to larger, cauliflower-like clusters.
The transmission of genital warts occurs through sexual contact, making them a significant public health concern. While they are generally not painful, they can cause itching, discomfort, and emotional distress. It's important to note that not everyone infected with HPV will develop genital warts, as the virus can remain dormant for years.
Treatment for genital warts may involve prescription topical medications, cryotherapy, or laser treatment. In some cases, surgical removal may be necessary. Practicing safe sex and receiving the HPV vaccine can help prevent the spread of genital warts and other HPV-related conditions.
How Do HPV Warts Spread?
HPV warts spread primarily through direct contact with an infected person or through contact with surfaces contaminated by the virus. This can occur through skin-to-skin contact, such as shaking hands or touching the infected area, or by touching objects like towels, razors, or shower floors that have been exposed to the virus.
The virus enters the body through small cuts, abrasions, or breaks in the skin, making it important to practice good hygiene and take precautions to prevent infection. Certain environments, such as public swimming pools, locker rooms, and communal showers, are more conducive to the spread of HPV due to their warm, moist conditions.
To minimize the risk of spreading or contracting HPV warts, individuals should avoid sharing personal items, keep the affected area clean and covered, and refrain from picking or scratching warts. Using protective footwear in communal areas and practicing safe sex can also help reduce the risk of transmission.
Diagnosis of HPV Warts: What to Expect
Diagnosing HPV warts typically involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. The visual appearance of the warts is often sufficient for diagnosis, as each type of wart has distinct characteristics. In some cases, a biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis, especially if the wart has an unusual appearance or if there is a risk of skin cancer.
During the examination, the healthcare provider will ask about the patient's medical history, including any previous occurrences of warts or HPV infections. They may also inquire about the patient's lifestyle, such as their hygiene habits or exposure to communal environments, to assess the risk of spreading the virus.
If genital warts are suspected, additional tests may be conducted, such as a Pap smear or HPV test, to check for other HPV-related conditions. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing HPV warts effectively and preventing further spread of the virus.
Treatment Options for HPV Warts
Treatment for HPV warts varies depending on the type, location, and severity of the warts. Common treatments include:
- Topical medications: Over-the-counter treatments like salicylic acid can help remove warts by softening the infected skin. Prescription medications, such as imiquimod or podophyllotoxin, may be recommended for genital warts.
- Cryotherapy: This involves freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen, causing the tissue to die and eventually fall off. Cryotherapy is commonly used for common, plantar, and filiform warts.
- Laser treatment: A focused beam of light is used to destroy the wart tissue. This method is effective for stubborn or difficult-to-treat warts.
- Surgical removal: In some cases, surgical excision or curettage may be necessary to remove large or persistent warts.
It's important to follow the healthcare provider's recommendations for treatment and to attend follow-up appointments to monitor the progress. While treatment can help remove warts, it may not eliminate the underlying virus, and warts can recur.
Can HPV Warts Be Prevented?
While it may not be possible to prevent all HPV wart infections, there are several measures individuals can take to reduce their risk:
- Vaccination: The HPV vaccine can protect against the strains of HPV most commonly associated with genital warts and certain types of cancer.
- Practice good hygiene: Regular handwashing, keeping the skin clean and dry, and avoiding touching warts can help prevent the spread of the virus.
- Avoid sharing personal items: Do not share towels, razors, or other personal items with others to reduce the risk of transmission.
- Use protective footwear: Wear flip-flops or sandals in communal showers, locker rooms, and swimming pool areas.
- Practice safe sex: Using condoms and having open conversations about sexual health can help prevent the spread of genital warts.
By taking these precautions, individuals can minimize their risk of contracting or spreading HPV warts and maintain overall skin health.
Are There Any Home Remedies for HPV Warts?
Several home remedies are often touted for their effectiveness in treating HPV warts, although their success may vary from person to person. Some popular home remedies include:
- Duct tape: Covering the wart with duct tape can help suffocate and gradually remove the wart. This method requires patience and consistency.
- Apple cider vinegar: Soaking a cotton ball in apple cider vinegar and applying it to the wart may help dissolve the infected skin over time.
- Garlic: Applying crushed garlic to the wart and covering it with a bandage may help reduce its size and appearance.
- Banana peel: Rubbing the inside of a banana peel on the wart is believed to help soften and remove it.
While these remedies may provide relief for some, it's important to consult with a healthcare provider before trying home treatments, especially for warts in sensitive areas like the face or genitals. Professional medical treatment is recommended for persistent or painful warts.
When Should I See a Doctor?
While many HPV warts can be managed with over-the-counter treatments or home remedies, there are instances when professional medical care is necessary. You should consider seeing a doctor if:
- The wart is painful, bleeding, or showing signs of infection.
- The wart changes in appearance or color.
- The wart does not respond to home treatment after a few weeks.
- You have multiple warts or they are spreading rapidly.
- The wart is located on the face, genitals, or another sensitive area.
Seeking medical advice ensures that the wart is treated effectively and any underlying conditions are addressed. A healthcare provider can recommend the most appropriate treatment options and provide guidance on preventing the spread of warts.
Lifestyle and Dietary Changes to Manage HPV Warts
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and making certain dietary changes can support the immune system and help manage HPV warts. Consider incorporating the following habits into your routine:
- Balanced diet: Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains to provide essential nutrients that support immune health.
- Regular exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to boost circulation and enhance immune function.
- Adequate sleep: Ensure you get enough rest each night to support overall health and recovery.
- Stress management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to maintain mental well-being.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to keep the skin hydrated and support overall health.
By adopting these healthy habits, individuals can strengthen their immune system, making it easier to fight off infections and manage HPV warts effectively.
Impact of HPV Warts on Mental Health
HPV warts, especially those in visible or sensitive areas, can have a significant impact on an individual's mental health. The presence of warts may lead to feelings of embarrassment, self-consciousness, and anxiety, affecting one's social interactions and overall quality of life.
It's important to acknowledge these feelings and seek support from trusted friends, family, or mental health professionals if necessary. Open communication about the condition with partners or loved ones can also help alleviate concerns and foster understanding.
Engaging in self-care practices, such as mindfulness and relaxation techniques, can help manage stress and improve mental well-being. Remember that HPV warts are a common condition, and with proper treatment and support, they can be effectively managed.
FAQs
What causes HPV warts to develop?
HPV warts develop due to infection with the human papillomavirus, which enters the skin through small cuts or abrasions. The virus causes the skin cells to grow rapidly, leading to the formation of warts.
Are all warts caused by HPV?
Most warts are caused by HPV, but not all. Some skin growths may resemble warts but are due to other causes, such as skin tags or molluscum contagiosum. A healthcare provider can help determine the exact cause of any skin growths.
Can HPV warts go away on their own?
In some cases, HPV warts may resolve on their own as the immune system fights off the virus. However, this can take months or even years, and treatment may be necessary to remove the warts and prevent their spread.
Is it possible to have HPV without showing symptoms?
Yes, many individuals with HPV may not show any symptoms, as the virus can remain dormant in the body. This is why regular screenings and practicing safe sex are important for preventing the spread of the virus.
Can I get HPV warts from a swimming pool?
While it's possible to contract HPV warts from surfaces in communal swimming areas, the risk is relatively low. Practicing good hygiene and wearing protective footwear can help minimize the risk of transmission.
Do HPV warts increase the risk of cancer?
Most HPV warts do not increase the risk of cancer. However, certain strains of HPV, particularly those associated with genital warts, can lead to cancers such as cervical, anal, or throat cancer. Regular screenings and vaccination can help reduce this risk.
Conclusion
HPV wart types encompass a range of skin growths that can affect individuals of all ages. Understanding the different types of warts, their causes, and available treatment options is essential for effective management and prevention. While HPV warts can be a source of discomfort and embarrassment, they are generally treatable, and with the right approach, individuals can minimize their impact on daily life.
By practicing good hygiene, seeking appropriate medical advice, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, individuals can reduce their risk of developing HPV warts and prevent their spread. Remember that you're not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you navigate the challenges associated with HPV warts.
For more information on HPV and related health topics, consider visiting reputable sources such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
Article Recommendations