Skin Cancer Face: Understanding, Prevention, And Treatment Options
Skin cancer is a serious health condition that can affect anyone, regardless of age or skin type. On the face, it can be particularly concerning due to the area’s exposure to the sun and its cosmetic implications. With the increasing awareness of skin cancer and its potential to be life-threatening, it's essential to understand the risks, preventative measures, and treatment options available. This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about skin cancer on the face, providing insights into the types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and more.
Being the most exposed part of the body, the face often bears the brunt of ultraviolet (UV) radiation, making it a common site for skin cancer development. While skin cancer is a common condition, affecting millions worldwide, early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. This article delves into the specifics of skin cancer on the face, helping you recognize warning signs early and advocating for regular dermatological check-ups as a preventive measure.
Moreover, understanding the psychological and emotional impact of facial skin cancer is crucial. Treatments not only focus on eradicating cancerous cells but also on preserving the patient’s appearance and self-esteem. By shedding light on the latest advancements in treatment and reconstruction, this guide aims to empower patients and their families with knowledge, aiding them in making informed decisions about their health.
Read also:All About Karlie Kloss The Model Entrepreneur And Philanthropist
Table of Contents
- What is Skin Cancer?
- Causes of Skin Cancer on the Face
- Types of Skin Cancer Affecting the Face
- What are the Early Signs and Symptoms?
- Diagnosis Methods for Skin Cancer Face
- What are the Treatment Options?
- Effective Prevention Strategies
- Impact on Appearance and Psychology
- Reconstructive Options After Treatment
- Why are Regular Skin Checks Important?
- Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Prevention
- Common Myths About Skin Cancer
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- External Link
What is Skin Cancer?
Skin cancer is a condition that arises from the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. It occurs when mutations in the DNA of skin cells cause the cells to multiply rapidly and form malignant tumors. The skin is composed of three primary layers: the epidermis, dermis, and subcutis. Skin cancer primarily affects the epidermis, the outer layer of the skin.
The primary types of skin cancer are basal cell carcinoma (BCC), squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and melanoma. While BCC and SCC are more common, melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer due to its tendency to spread to other parts of the body. Understanding the different types of skin cancers is crucial for recognizing symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
Causes of Skin Cancer on the Face
Several factors contribute to the development of skin cancer on the face, including:
- Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation: The most significant risk factor for skin cancer is UV radiation from the sun and tanning beds. Prolonged exposure to UV rays can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to cancer.
- Genetic Factors: Individuals with a family history of skin cancer are more susceptible. Certain genetic conditions, like xeroderma pigmentosum, also increase the risk.
- Fair Skin: People with lighter skin have less melanin, which provides some protection against UV radiation. As a result, they are at a higher risk of developing skin cancer.
- Age: The risk of skin cancer increases with age, as the cumulative exposure to UV radiation over time can lead to cellular damage.
Types of Skin Cancer Affecting the Face
Skin cancer on the face can manifest in various forms, each with distinct characteristics:
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
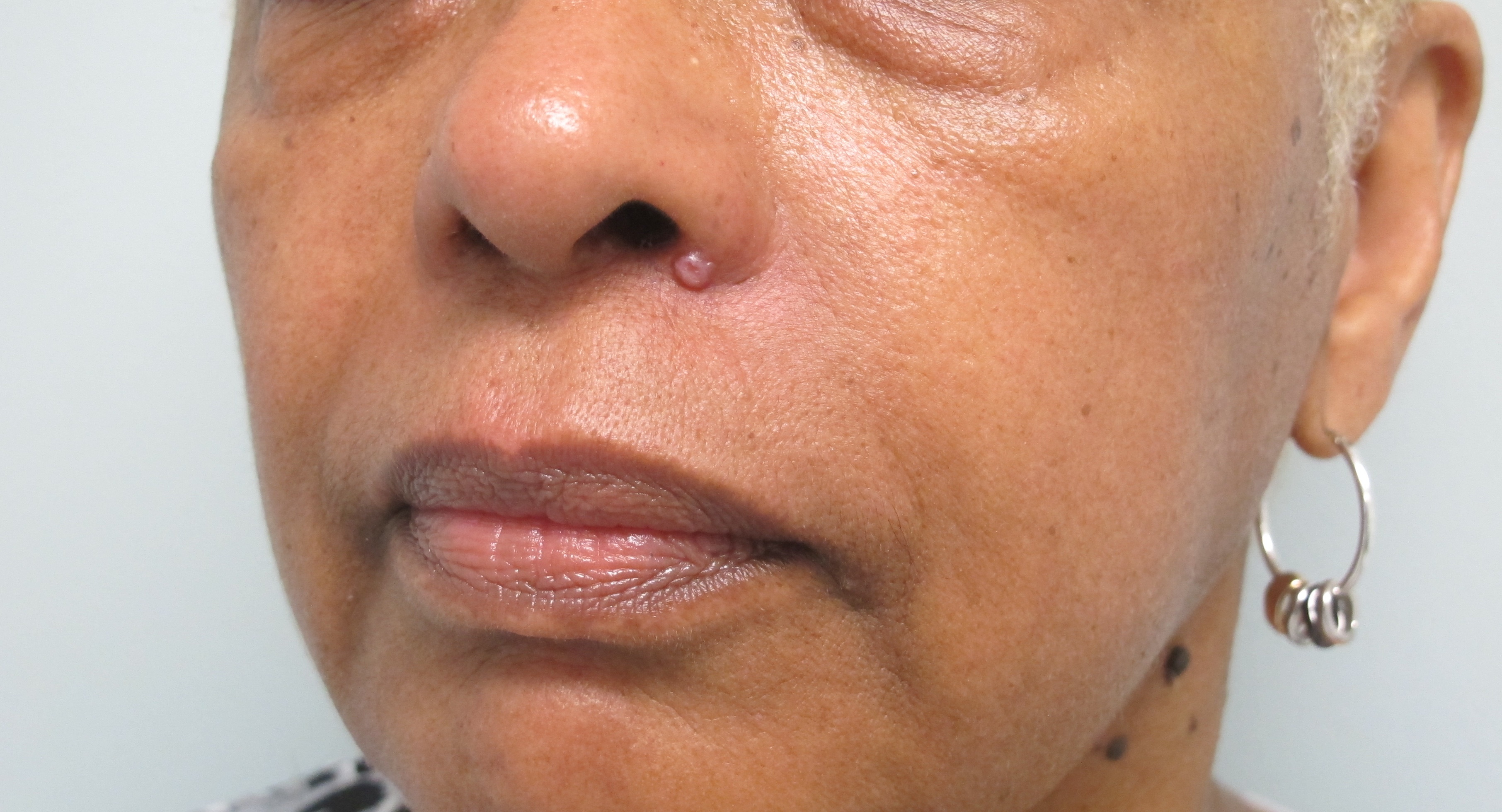
BCC is the most prevalent form of skin cancer, accounting for about 80% of cases. It often appears as a small, shiny bump or a pinkish patch on the face. BCC grows slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body, but it can cause significant damage to surrounding tissues if left untreated.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC)
SCC is the second most common type of skin cancer, making up approximately 20% of cases. It typically presents as a firm, red nodule or a rough, scaly patch on the skin. SCC can be more aggressive than BCC and has a higher likelihood of spreading to nearby lymph nodes if not treated promptly.
Read also:Remarkable Contributions Of Darius And Dominic Jones
Melanoma
Although less common, melanoma is the deadliest form of skin cancer. It can develop from an existing mole or appear as a new dark spot on the skin. Melanoma is known for its rapid growth and potential to metastasize to internal organs, making early detection and treatment vital.
What are the Early Signs and Symptoms?
Recognizing the early signs of skin cancer on the face is crucial for prompt treatment. Key symptoms to watch for include:
- New Growths: Any new lump, bump, or spot on the face that differs from the surrounding skin should be examined by a healthcare professional.
- Changes in Existing Moles: Pay attention to changes in size, shape, color, or texture of moles, as these can indicate melanoma.
- Non-Healing Sores: Sores that do not heal within a few weeks or that bleed easily may be indicative of skin cancer.
- Changes in Skin Texture: The development of rough or scaly patches, especially on sun-exposed areas, can be a sign of SCC.
Diagnosis Methods for Skin Cancer Face
Accurate diagnosis of skin cancer on the face is essential for effective treatment. Healthcare providers use various techniques and tools to diagnose skin cancer:
Physical Examination
A thorough examination of the skin, particularly the face, is the first step. Dermatologists look for unusual growths, changes in moles, and other suspicious lesions.
Dermatoscopy
This non-invasive procedure involves using a dermatoscope, a handheld device that provides a magnified view of the skin. It aids in identifying suspicious features not visible to the naked eye.
Biopsy
If a lesion appears suspicious, a biopsy is performed. A small sample of the skin is removed and examined under a microscope to confirm the presence of cancerous cells.
What are the Treatment Options?
Treating skin cancer on the face requires a multifaceted approach, considering both the eradication of cancerous cells and cosmetic outcomes. Treatment options include:
Surgical Excision
The most common treatment involves surgically removing the cancerous tissue along with a margin of healthy skin. This method is effective for most types of skin cancer.
Mohs Surgery
Mohs micrographic surgery is a highly precise technique used for facial skin cancers. It involves removing the cancerous tissue layer by layer, examining each layer under a microscope until no cancerous cells remain.
Radiation Therapy
For patients who are not suitable candidates for surgery, radiation therapy may be used. It involves directing high-energy rays at the cancerous cells to destroy them.
Cryotherapy
In this method, liquid nitrogen is used to freeze and destroy superficial skin cancers. It is typically used for small, non-melanoma skin cancers.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Preventing skin cancer on the face involves adopting protective measures against UV radiation and fostering healthy skin practices:
- Sun Protection: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 daily, even on cloudy days. Wear wide-brimmed hats and sunglasses for added protection.
- Avoid Tanning Beds: Tanning beds expose the skin to harmful UV rays, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
- Regular Skin Checks: Perform monthly self-examinations and schedule annual skin checks with a dermatologist to catch any suspicious changes early.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, which can help protect skin cells from damage.
Impact on Appearance and Psychology
Skin cancer on the face can have a profound impact on a person’s appearance and psychological well-being. The visible nature of the disease often leads to emotional distress, affecting self-esteem and social interactions. Addressing these concerns is a vital part of the treatment process.
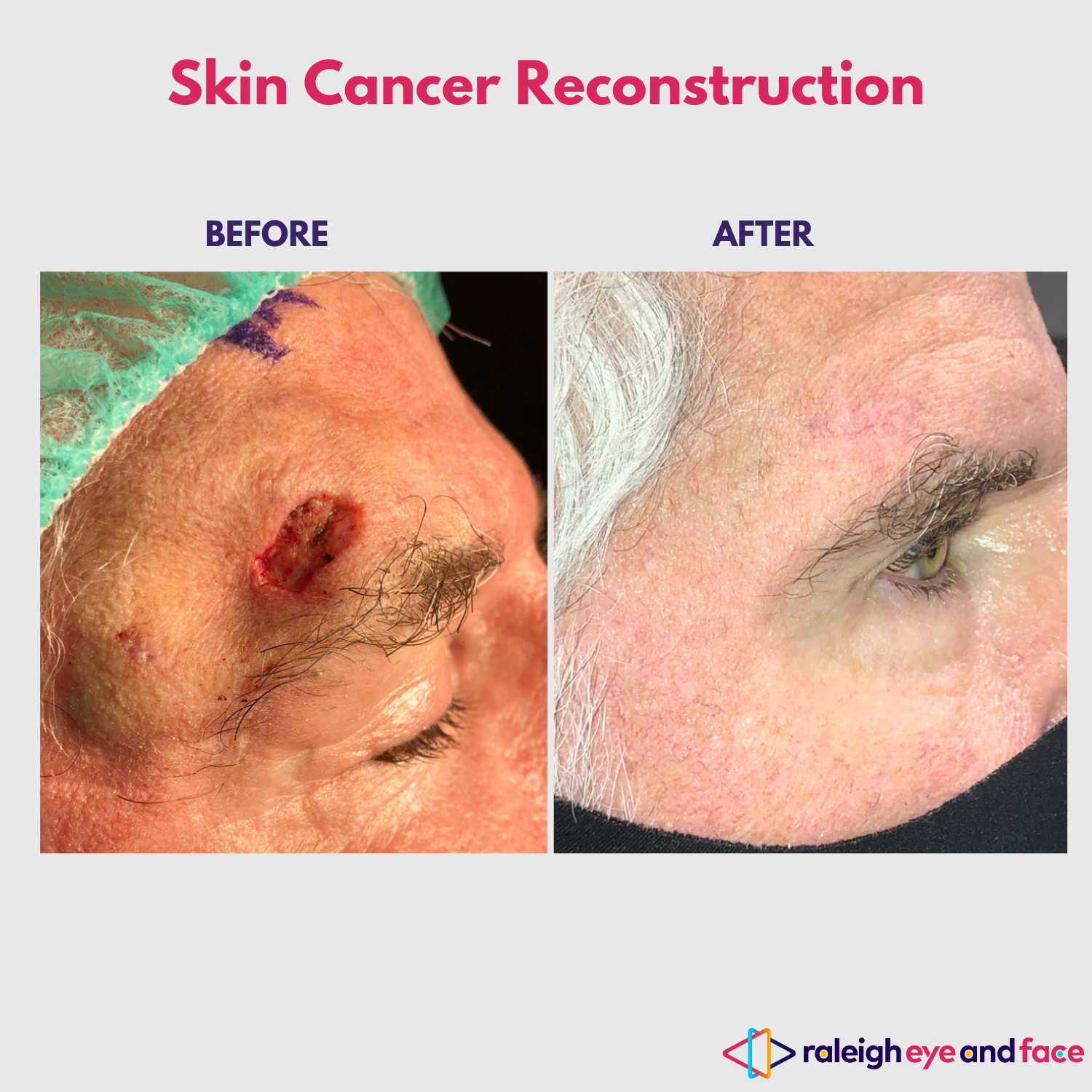
Reconstructive Options After Treatment
Reconstruction plays a critical role in the treatment of facial skin cancer, especially after surgical excision. Techniques vary depending on the size and location of the excision, aiming to restore facial symmetry and function while minimizing scarring.
Why are Regular Skin Checks Important?
Regular skin checks are essential for early detection and successful treatment of skin cancer. They allow for the identification of changes or new growths that could indicate malignancy, enabling prompt intervention.
Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Prevention
Diet and lifestyle choices play a significant role in skin cancer prevention. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can bolster skin health and provide protection against cellular damage from UV exposure.
Common Myths About Skin Cancer
Several misconceptions surround skin cancer, leading to inadequate protection and delayed diagnosis. Addressing these myths is crucial for spreading awareness and promoting proactive skin health measures.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can skin cancer on the face be cured? Yes, most cases of skin cancer can be cured, especially when detected and treated early.
- Is it possible to prevent skin cancer? While not all cases are preventable, reducing UV exposure and adopting healthy skin practices can significantly lower the risk.
- What is the most effective treatment for facial skin cancer? The effectiveness of treatment depends on the type and stage of cancer. Surgical excision and Mohs surgery are commonly used for facial skin cancers.
- How often should I have my skin checked? It's recommended to have skin checks annually with a dermatologist, along with monthly self-examinations.
- Are there any natural remedies for skin cancer? No, there are no proven natural remedies for treating skin cancer. Professional medical treatment is necessary.
- What should I do if I notice a suspicious spot on my face? If you notice any new or changing spots on your face, consult a dermatologist for a professional evaluation.
Conclusion
Understanding skin cancer on the face is crucial for prevention, early detection, and effective treatment. By adopting protective measures, such as using sunscreen and avoiding tanning beds, individuals can significantly reduce their risk. Regular skin checks and awareness of changes in the skin are vital for catching skin cancer in its early stages, where treatment is most successful. Through a combination of medical treatment and lifestyle changes, those affected by skin cancer on the face can achieve positive outcomes and maintain their quality of life.
External Link
For more information on skin cancer, visit the American Cancer Society.
Article Recommendations