The Essential Guide To Skin Cancer On The Face: Prevention, Detection, And Treatment
The face, a prominent area of our body, is often exposed to sunlight, making it susceptible to skin damage and cancer. Despite the alarming statistics, many people still neglect proper sun protection, increasing their risk of developing skin cancer on the face. Understanding the importance of early detection and the available treatment options can significantly impact outcomes and improve survival rates. In this article, we will explore the various facets of skin cancer on the face, including its types, stages, warning signs, and preventive strategies. We will also discuss the latest advancements in treatment, the role of dermatologists, and how lifestyle choices can influence risk levels. Whether you're seeking to protect yourself or a loved one, this comprehensive guide will provide valuable insights to help you stay informed and proactive.
What is Skin Cancer?
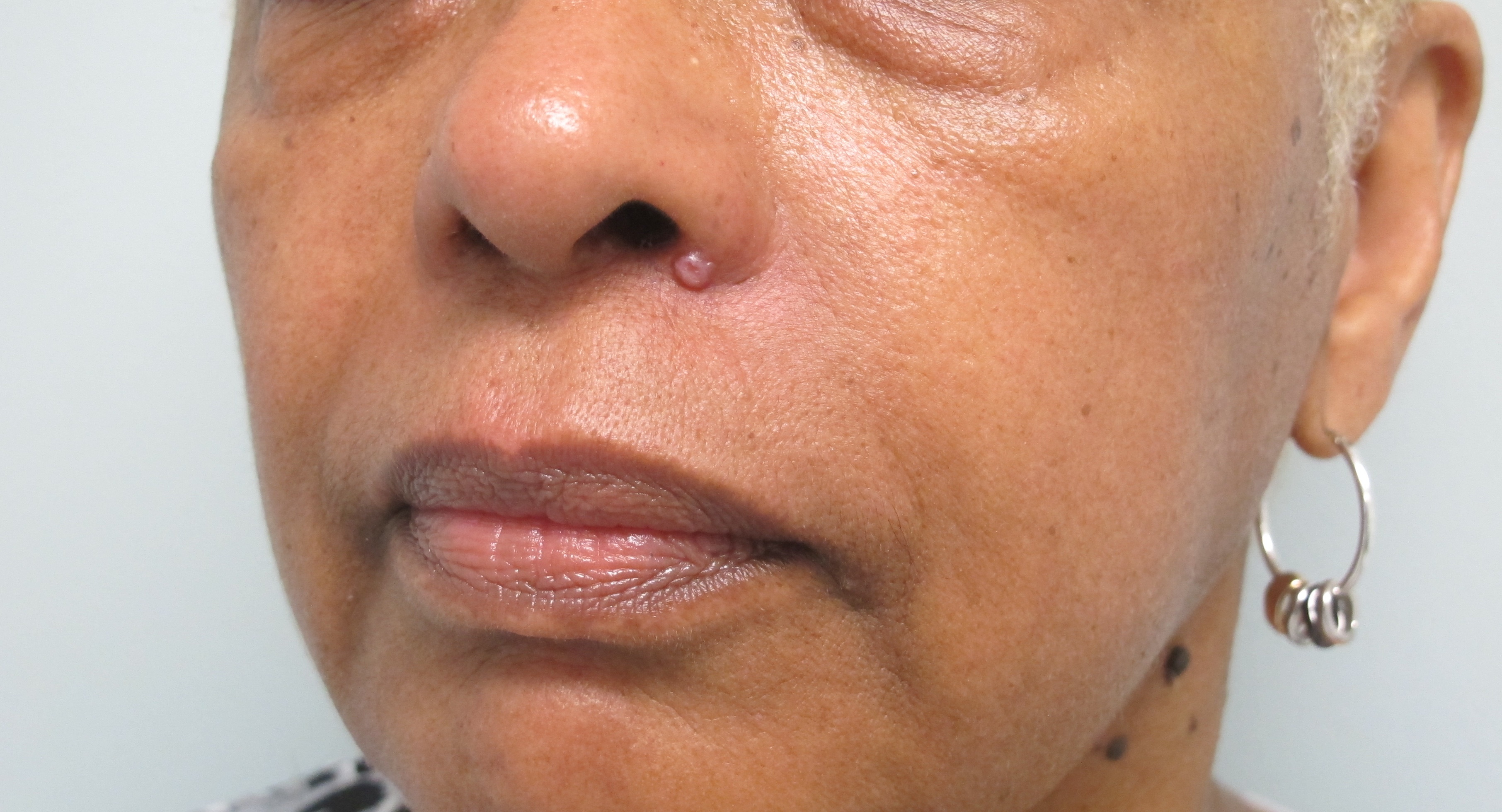
Skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells, usually developing on skin exposed to the sun. However, it can also occur in areas not ordinarily exposed to sunlight. Skin cancer primarily affects the epidermis, the outermost layer of skin, where it is often visible, allowing for early detection. There are three main types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma.
Basal cell carcinoma is the most common form and often appears as a waxy bump. Squamous cell carcinoma typically presents as a firm, red nodule or a flat lesion with a scaly, crusted surface. Melanoma, though less common, is the most serious type of skin cancer, characterized by moles that change in color, size, or feel, or that bleed. Early diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and to prevent the cancer from spreading to other parts of the body.
Read also:Maximize Savings With Spirit Halloween Coupons And Deals
Understanding the different types of skin cancer and their symptoms is essential in recognizing potential issues early. Regular self-examinations and professional skin checks are vital components of a proactive approach to skin health.
Types of Skin Cancer on the Face
Basal Cell Carcinoma
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) is the most common type of skin cancer on the face, accounting for about 80% of all skin cancer cases. It originates from the basal cells, which are found in the lower part of the epidermis. BCC often appears as a small, shiny bump or nodule on the face, particularly in areas that receive a lot of sun exposure. While it rarely metastasizes, it can cause significant local damage if not treated promptly.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is the second most common type of skin cancer on the face. It arises from the squamous cells, which make up most of the skin's upper layers. SCC often manifests as a rough, scaly patch or a wart-like growth that may crust or bleed. It is more aggressive than BCC and can spread to other parts of the body if not treated early.
Melanoma
Melanoma is the most dangerous form of skin cancer, known for its ability to spread to other organs quickly. On the face, melanoma may appear as a new mole or an existing mole that changes in appearance. Key warning signs include asymmetry, irregular borders, multiple colors, a diameter larger than a pencil eraser, and evolving shape or size. Although less common than BCC and SCC, melanoma accounts for the majority of skin cancer deaths due to its aggressive nature.
Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Merkel cell carcinoma is a rare but aggressive form of skin cancer that usually appears as a painless, flesh-colored or bluish-red nodule on the face, head, or neck. It is more common in older individuals and those with weakened immune systems. Due to its rapid growth and potential to spread, early detection and treatment are crucial.
Risk Factors for Skin Cancer
Several factors can increase the risk of developing skin cancer on the face, including:
Read also:Guiding Light 858 Angel Number Meaning And Its Profound Impact
- Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun or tanning beds.
- Fair skin, light hair, and eye color, which provide less natural protection against UV rays.
- History of sunburns, particularly in childhood or adolescence.
- Family history of skin cancer, indicating a possible genetic predisposition.
- Presence of many moles or atypical moles, which can develop into melanoma.
- Weakened immune system, due to conditions such as HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive drugs.
Understanding these risk factors can help individuals take proactive measures to reduce their chances of developing skin cancer. Regular use of sunscreen, protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun exposure times are effective strategies for minimizing risk.
How to Prevent Skin Cancer on the Face?
What Are Effective Sun Protection Strategies?
Sun protection is the cornerstone of skin cancer prevention. Implementing the following strategies can significantly reduce your risk:
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, even on cloudy days.
- Wear wide-brimmed hats and UV-blocking sunglasses.
- Seek shade during peak sun hours, typically between 10 AM and 4 PM.
- Avoid tanning beds, which emit harmful UV radiation.
- Wear protective clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and long pants, made from tightly woven fabrics.
How Often Should You Perform Skin Self-Exams?
Regular self-examinations are essential for early detection of skin cancer. The American Cancer Society recommends performing a skin self-exam once a month. During the exam, carefully check all areas of your body, including your face, ears, and neck, for new growths or changes in existing moles. Use a mirror to examine hard-to-see areas, and consider asking a partner or friend to help with the examination.
If you notice any suspicious changes, such as a new mole or a mole that changes in size, shape, or color, consult a dermatologist promptly for further evaluation.
Early Detection and Warning Signs
Early detection of skin cancer on the face can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Key warning signs to watch for include:
- A new growth or sore that doesn't heal within a few weeks.
- Changes in the size, shape, or color of an existing mole.
- Redness or swelling beyond the border of a mole.
- Itching, tenderness, or pain in a mole or surrounding area.
- Scaliness, oozing, or bleeding from a mole or growth.
The ABCDE rule is a helpful guide for identifying potential melanoma:
- Asymmetry: One half of the mole doesn't match the other.
- Border: Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined edges.
- Color: Varied shades of brown, black, or other colors.
- Diameter: Larger than 6mm (about the size of a pencil eraser).
- Evolving: Changes in size, shape, or color over time.
Diagnosis and Staging
When a dermatologist suspects skin cancer, they will perform a thorough examination and may order a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small sample of the suspicious tissue is removed and analyzed under a microscope. If skin cancer is diagnosed, further tests may be conducted to determine the cancer's stage and extent of spread.
Staging is crucial for guiding treatment decisions and is based on factors such as the size and depth of the tumor, whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes, and if it has metastasized to other parts of the body. The most common staging system is the TNM system, which considers the Tumor size, Node involvement, and Metastasis.
Treatment Options for Skin Cancer
Treatment for skin cancer on the face depends on the type, stage, and location of the cancer and may include one or more of the following options:
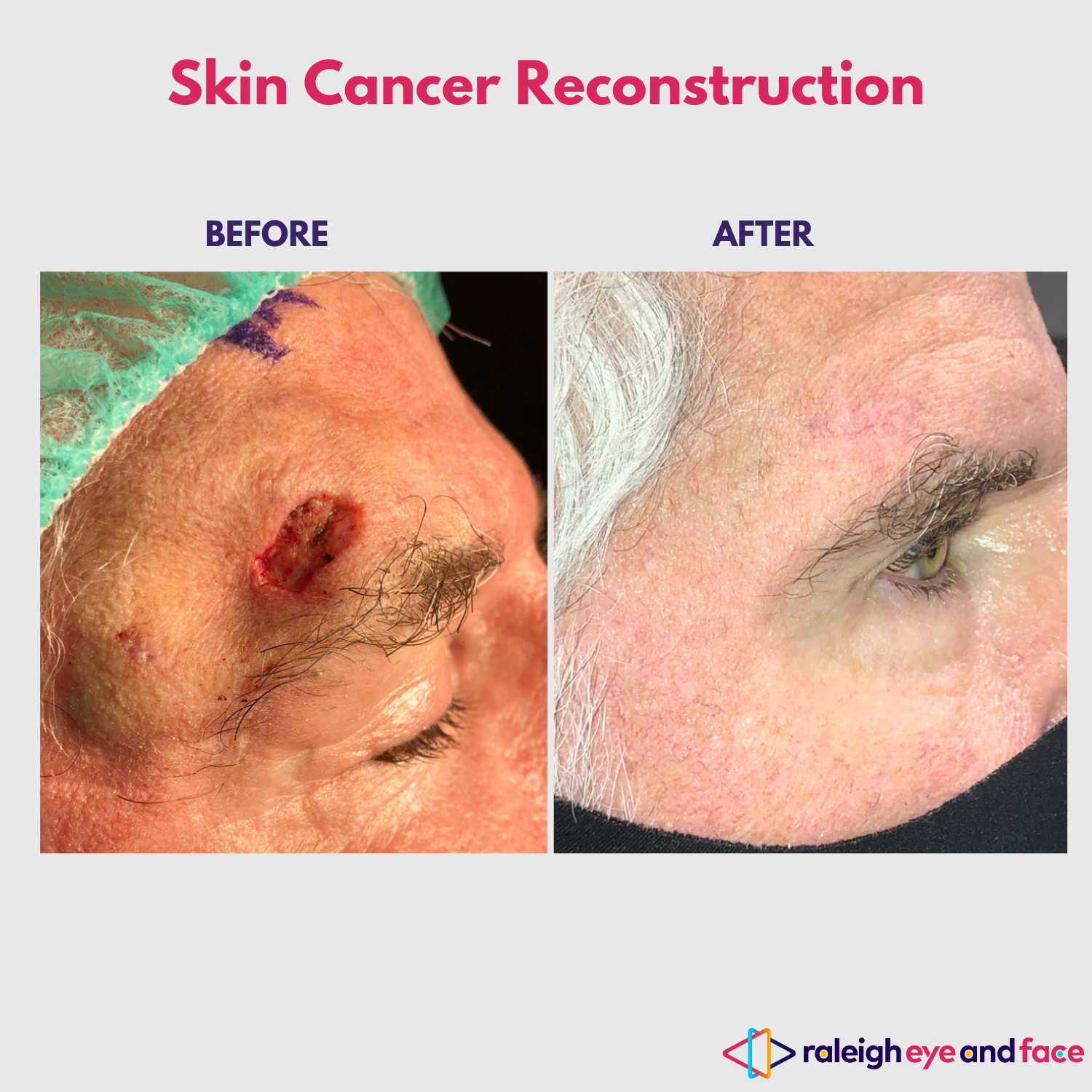
- Surgical Excision: The cancerous tissue is surgically removed along with a margin of healthy tissue to ensure complete removal.
- Mohs Surgery: A precise surgical technique in which thin layers of cancerous tissue are removed and examined until no cancer cells remain.
- Cryotherapy: The cancerous tissue is frozen using liquid nitrogen, causing it to slough off.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy rays are used to target and destroy cancer cells, often used for cancers in challenging locations or for patients who cannot undergo surgery.
- Topical Treatments: Creams or ointments are applied to the skin to treat superficial skin cancers.
- Immunotherapy: Boosts the immune system's ability to fight cancer, often used for advanced melanoma.
- Chemotherapy: Uses drugs to kill cancer cells, typically reserved for advanced or metastatic cancer.
Role of Dermatologists in Skin Cancer Treatment
Dermatologists play a crucial role in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of skin cancer on the face. They are trained to identify and evaluate suspicious lesions, perform biopsies, and recommend appropriate treatment options based on the cancer type and stage.
In addition to providing medical treatment, dermatologists educate patients on sun protection strategies and skin cancer prevention. They may also perform regular skin checks for individuals at high risk of developing skin cancer, ensuring early detection and intervention.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Risk
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the risk of developing skin cancer on the face:
- Limit sun exposure, especially during peak hours, and consistently apply sunscreen.
- Adopt a healthy diet rich in antioxidants, which can help protect skin cells from UV damage.
- Stay hydrated to maintain skin health and resilience.
- Avoid smoking, which can damage skin and increase cancer risk.
- Regularly monitor skin for changes and seek medical advice for any concerns.
Emerging Research and Advancements
Research in skin cancer treatment and prevention is continuously evolving, with promising advancements on the horizon. Innovations in genetic testing and personalized medicine are paving the way for more targeted and effective treatments, reducing the need for invasive procedures.
Additionally, researchers are exploring the potential of artificial intelligence in early skin cancer detection, improving diagnostic accuracy and facilitating timely intervention. Ongoing studies are also examining the role of lifestyle factors, such as diet and exercise, in reducing cancer risk and supporting overall skin health.
Impact of Skin Cancer on Mental Health
Receiving a skin cancer diagnosis can have a significant impact on an individual's mental and emotional well-being. Concerns about treatment, prognosis, and changes to appearance can lead to feelings of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Support from healthcare professionals, loved ones, and support groups can be invaluable in helping individuals cope with the emotional challenges of skin cancer. Mental health counseling and therapy may also be beneficial for those struggling to adapt to the changes and uncertainties associated with their diagnosis.
Support Networks and Resources
Accessing support networks and resources is crucial for individuals affected by skin cancer. Organizations such as the Skin Cancer Foundation and the American Academy of Dermatology provide educational materials, support groups, and advocacy for patients and families.
Online forums and local support groups can offer a sense of community and shared experiences, providing emotional comfort and practical advice. Healthcare professionals can also connect patients with counseling and mental health services to support their overall well-being.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the early signs of skin cancer on the face?
Early signs include new growths, changes in existing moles, and sores that don't heal. Look for asymmetry, irregular borders, varied colors, and changes in size or shape.
How is skin cancer on the face diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination and a biopsy, where a small sample of the suspicious tissue is analyzed under a microscope.
Can skin cancer on the face spread to other parts of the body?
Yes, especially melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma, which can metastasize if not detected and treated early.
What are the treatment options for skin cancer on the face?
Treatment options include surgical excision, Mohs surgery, cryotherapy, radiation therapy, topical treatments, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy, depending on the cancer type and stage.
How can I reduce my risk of developing skin cancer on the face?
Practice sun protection, avoid tanning beds, perform regular skin checks, and make healthy lifestyle choices such as maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding smoking.
What role do dermatologists play in managing skin cancer?
Dermatologists diagnose, treat, and manage skin cancer, providing medical care, education on prevention, and regular skin examinations for high-risk individuals.
Conclusion
Skin cancer on the face is a prevalent and potentially serious condition, but with early detection and proper management, outcomes can be significantly improved. Understanding the risk factors, symptoms, and preventive measures is essential for protecting yourself and your loved ones. By staying informed, practicing sun safety, and seeking regular dermatological care, you can reduce your risk and ensure the health of your skin.
Remember, the key to combating skin cancer lies in awareness and proactive measures. By incorporating the insights from this comprehensive guide into your daily routine, you are taking an important step towards safeguarding your skin and overall well-being.
Article Recommendations