Mastering Roman Numerals VIX: A Guide To Understanding Ancient Numbering
Roman numerals have a rich history and have been used for centuries to represent numbers in a variety of contexts. The Roman numeral system, originating in ancient Rome, is a numeric system based on the Latin alphabet, utilizing combinations of letters such as I, V, X, L, C, D, and M. These numerals are still in use today, often seen in clock faces, book chapters, and even in the naming of monarchs and popes. Despite their historical roots, Roman numerals continue to be relevant in modern times, offering a glimpse into the past while maintaining a timeless elegance.
In the world of Roman numerals, "VIX" is a specific combination that stands out. While it may seem straightforward, understanding how Roman numerals work is essential to deciphering this combination correctly. Roman numerals use a system of addition and subtraction to represent numbers. For example, the numeral "V" represents the number 5, "I" represents the number 1, and "X" represents the number 10. The order and placement of these numerals affect their overall value, leading to interesting combinations like VIX.
Mastering Roman numerals, especially combinations like VIX, requires a grasp of the fundamental principles of this ancient numbering system. This article delves into the intricacies of Roman numerals, offering a detailed guide on how to read, write, and understand them. From their historical origins to their practical applications today, this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the information you need to become proficient in the world of Roman numerals. Let's embark on a journey to uncover the mysteries of Roman numerals, starting with the intriguing combination of VIX.
Read also:Who Is Lele Pons A Deep Dive Into Her Life And Career
Table of Contents
- History of Roman Numerals
- What Are Roman Numerals?
- How Do Roman Numerals Work?
- The Significance of VIX
- How to Write and Read VIX?
- Common Mistakes with VIX
- Applications of Roman Numerals in Modern Times
- Roman Numerals in Pop Culture
- Educational Benefits of Learning Roman Numerals
- Teaching Roman Numerals to Children
- Roman Numerals in Different Cultures
- The Future of Roman Numerals
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
History of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system has a fascinating history that dates back to ancient Rome, around the 8th century BC. It was developed as a means of counting and conducting trade. Unlike our modern decimal system, Roman numerals are not based on place value, but rather on a combination of letters from the Latin alphabet. The numbers are represented by seven different symbols: I, V, X, L, C, D, and M.
These symbols were used extensively in the Roman Empire for various purposes, including in commerce, architecture, and legal documentation. Roman numerals were also used in inscriptions on buildings and monuments, many of which still stand today, offering insights into the mathematical conventions of the time. The system was efficient for the Romans' needs, with its simplicity and ease of use making it particularly suitable for addition and subtraction.
The significance of Roman numerals extends beyond their practical applications. They hold cultural and historical value, as they are closely associated with the Roman Empire's legacy. Over the centuries, the use of Roman numerals spread throughout Europe and became deeply embedded in Western culture. Even with the advent of the Arabic numeral system, Roman numerals have persisted due to their stylistic and symbolic appeal.
What Are Roman Numerals?
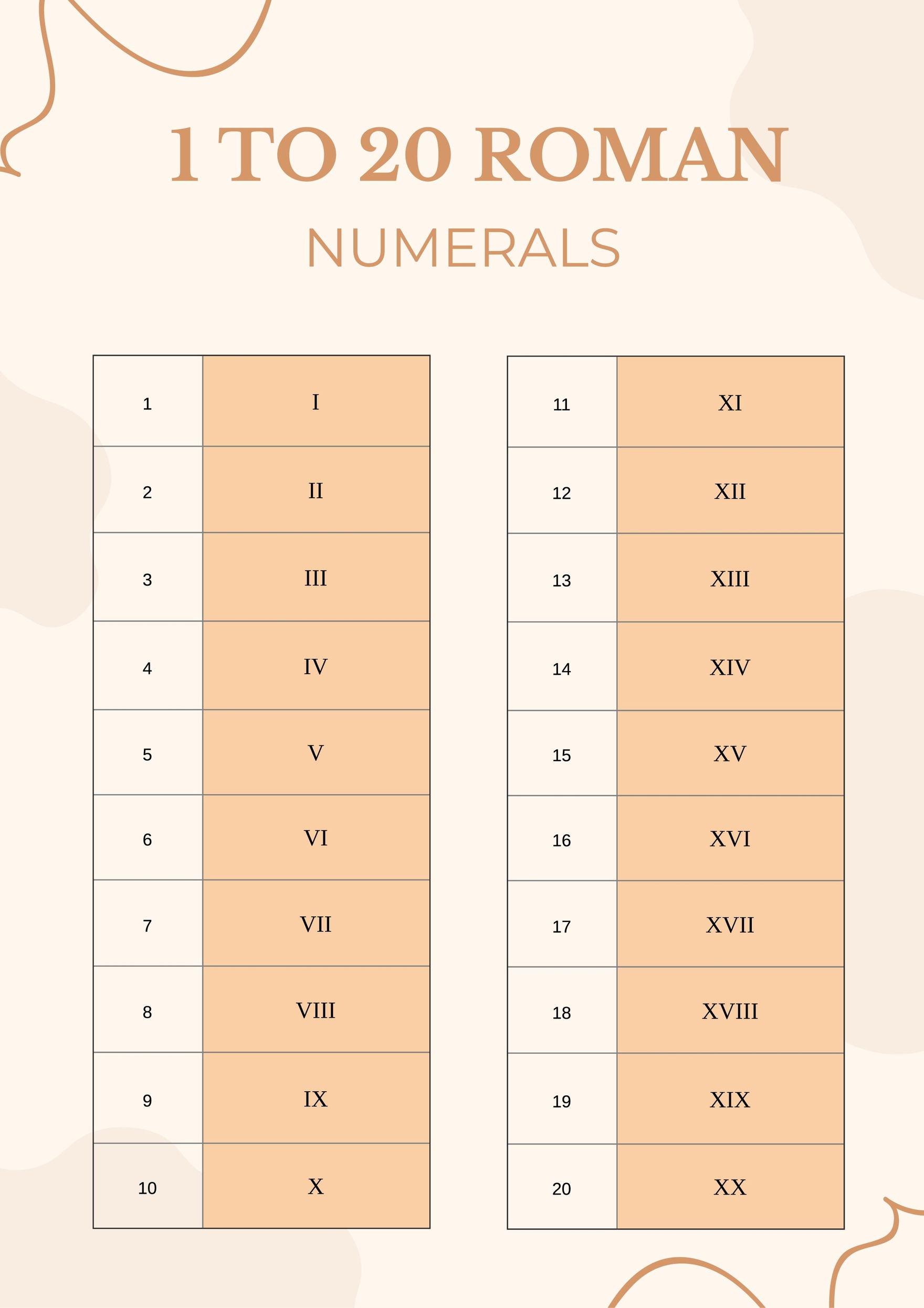
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and are used throughout Europe. This system uses combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet to represent numbers. The Roman numeral system is based on seven symbols, each with a fixed integer value:
- I - 1
- V - 5
- X - 10
- L - 50
- C - 100
- D - 500
- M - 1000
These numerals are combined to create other numbers. For example, the numeral for two is written as "II," which is simply two ones added together. The numeral for four is "IV," which indicates that one is subtracted from five. This system of addition and subtraction allows for the creation of a variety of combinations to represent different numbers.
Understanding Roman numerals involves knowing the rules for their formation. The order of the numerals is crucial, as it determines whether the values are added or subtracted. Generally, if a smaller numeral appears in front of a larger one, it is subtracted; if it appears after, it is added. This system, while ancient, remains intuitive and is still taught in schools today.
Read also:Adventurous Wild Rivers Natures Untamed Waterways
How Do Roman Numerals Work?
Roman numerals work based on a system of addition and subtraction. To understand how they function, it's important to grasp the fundamental rules that govern their use. The basic principle is that the value of the numerals is determined by their position and the relation to surrounding numerals.
Here are the key rules for reading and writing Roman numerals:
- If a smaller numeral is placed before a larger numeral, you subtract the smaller numeral. For instance, IV means 4 (5 - 1).
- If a smaller numeral is placed after a larger numeral, you add the smaller numeral. For example, VI means 6 (5 + 1).
- Do not use the same numeral more than three times in succession. Instead, use subtraction. For instance, 4 is IV, not IIII.
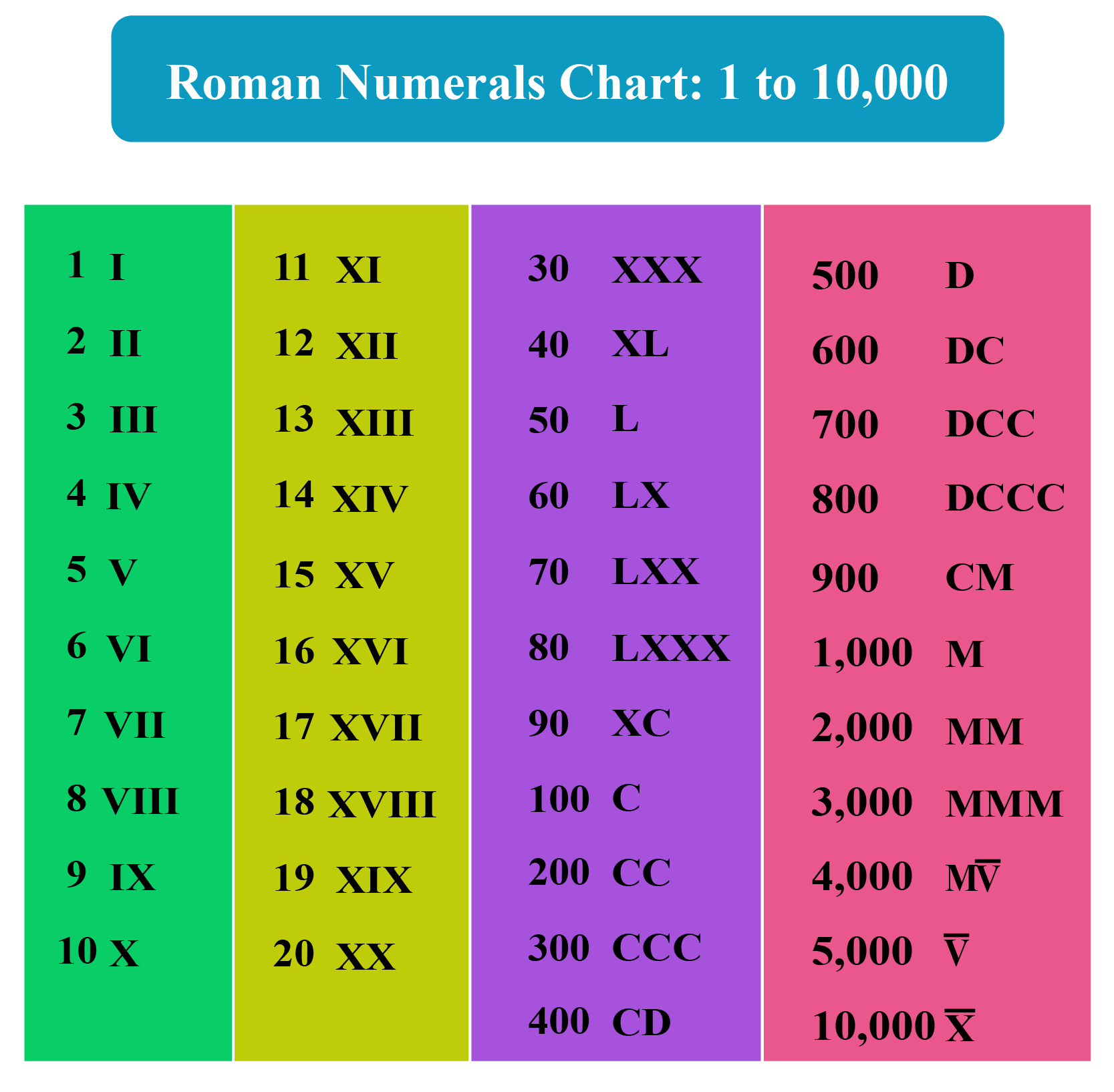
- When writing large numbers, a bar placed over a numeral multiplies its value by 1,000. For instance, V̅ equals 5,000.
These rules make it possible to represent a wide range of numbers using Roman numerals. Although they lack a numeral for zero, the system is still functional for many purposes, particularly in contexts where simplicity and clarity are valued, such as on clock faces or in outlines.
The Significance of VIX
In the context of Roman numerals, "VIX" is an intriguing combination that piques the interest of enthusiasts and students alike. Understanding the significance of VIX requires a comprehension of the principles of Roman numeral arithmetic. In this combination, "V" represents 5, "I" represents 1, and "X" represents 10.
To interpret "VIX" correctly, we apply the rules of Roman numerals. The correct reading of VIX is 9, which is derived from the sequence where 10 (X) is reduced by 1 (I), preceding the X, and then adding 5 (V). This gives us the equation: V (5) + (X - I) (9 - 1) = 9.
The significance of VIX also extends beyond its numeric value. It reflects the elegance and complexity of the Roman numeral system, showcasing how a seemingly simple arrangement of letters can encapsulate a deeper numeric logic. For those interested in historical mathematics or the cultural aspects of ancient Rome, VIX stands as a testament to the enduring legacy of Roman numerals.
How to Write and Read VIX?
Writing and reading VIX as Roman numerals involves a straightforward application of the basic principles of Roman numeral arithmetic. When faced with VIX, we must first break down the individual components and apply the rules of the system to determine their cumulative value.
Here is a step-by-step guide to understanding VIX:
- Identify the numerals: V (5), I (1), X (10).
- Apply the subtraction rule: Since I precedes X, subtract 1 from 10, resulting in 9.
- Add the remaining numeral: Add the value of V (5) to the result of the subtraction (9), resulting in the final value of 14.
While reading VIX, it is crucial to focus on the sequence and the rules governing the placement of numerals. This approach ensures an accurate interpretation of the combination, revealing the elegance and logic inherent in Roman numerals.
Common Mistakes with VIX
Working with Roman numerals, particularly combinations like VIX, can lead to common mistakes, especially for those who are not familiar with the rules of the system. Understanding these potential pitfalls is essential to prevent errors and gain a deeper comprehension of Roman numerals.
Some common mistakes include:
- Incorrect subtraction: Assuming that the subtraction rule applies to all numerals without considering their order can lead to errors. For example, reading VIX as 16 instead of 14 due to overlooking the subtraction aspect.
- Overuse of numerals: Using more than three identical numerals in succession, such as writing IIII instead of IV for 4, is a frequent error.
- Misinterpretation of numeral placement: Failing to recognize when to add or subtract based on the order of numerals can result in miscalculations.
By recognizing these common mistakes and taking the time to understand the logic behind Roman numerals, individuals can enhance their skills and reduce errors when interpreting combinations like VIX.
Applications of Roman Numerals in Modern Times
Despite being an ancient numbering system, Roman numerals have maintained their relevance in modern times across various applications. They continue to be used in areas where tradition, formality, or aesthetic appeal are valued, and they offer a distinctive touch to contemporary settings.
Some common applications of Roman numerals today include:
- Clocks and Watches: Roman numerals are often used on clock faces, adding a classic and timeless look to timepieces.
- Movie Sequels and Book Chapters: Roman numerals are frequently used to denote sequels in film franchises and chapter numbers in books, providing a sense of continuity and sophistication.
- Monarchs and Popes: Roman numerals are used in the naming conventions for monarchs and popes, such as Queen Elizabeth II and Pope John Paul II.
- Sporting Events: Major events like the Super Bowl use Roman numerals to denote the edition number, adding prestige and tradition to the occasion.
These applications demonstrate the enduring appeal of Roman numerals, highlighting their ability to bridge the gap between the past and the present while maintaining their cultural and historical significance.
Roman Numerals in Pop Culture
Roman numerals have made their mark on pop culture, appearing in various forms of media and entertainment. Their distinctive look and historical significance make them a popular choice for creators seeking to evoke a sense of antiquity or gravitas.
Examples of Roman numerals in pop culture include:
- Movie Titles: Films like "Rocky II" and "Star Wars Episode IV: A New Hope" use Roman numerals to denote sequels and episodes, adding an air of importance and continuity.
- Television Shows: Roman numerals are often used in episode titles or season numbers to create a sense of order and legacy.
- Video Games: Many video games, such as "Final Fantasy VII," incorporate Roman numerals in their titles to indicate series entries and maintain a cohesive identity.
- Music Albums: Artists sometimes use Roman numerals in album titles or track listings to impart a classic or sophisticated feel.
The use of Roman numerals in pop culture highlights their versatility and continued relevance, allowing them to remain an integral part of contemporary creative expression.
Educational Benefits of Learning Roman Numerals
Learning Roman numerals offers numerous educational benefits, making it a valuable addition to any curriculum. By studying this ancient system, students can develop a better understanding of history, mathematics, and cultural heritage.
The educational benefits of learning Roman numerals include:
- Historical Context: Roman numerals provide insight into the history and culture of ancient Rome, offering a glimpse into the mathematical conventions of the time.
- Mathematical Skills: Understanding Roman numerals helps students develop problem-solving skills and enhances their ability to work with non-decimal numbering systems.
- Cultural Awareness: Learning Roman numerals fosters an appreciation for cultural heritage and the enduring influence of the Roman Empire on modern society.
- Cognitive Development: Working with Roman numerals challenges students to think critically and logically, promoting cognitive growth and analytical thinking.
Through the study of Roman numerals, students can gain a deeper appreciation for mathematics and history, equipping them with valuable skills that can be applied across various disciplines.
Teaching Roman Numerals to Children
Introducing Roman numerals to children can be an engaging and educational experience. By incorporating fun activities and interactive learning methods, educators can help young learners grasp the principles of Roman numerals and appreciate their historical significance.
Effective strategies for teaching Roman numerals to children include:
- Games and Activities: Use games and puzzles that incorporate Roman numerals to make learning enjoyable and interactive.
- Visual Aids: Employ visual aids, such as charts and flashcards, to help children recognize and remember the symbols and their values.
- Storytelling: Share stories about ancient Rome and the origins of Roman numerals to capture children's interest and imagination.
- Real-World Examples: Highlight the use of Roman numerals in everyday life, such as on clocks and in movie titles, to demonstrate their continued relevance.
By using these strategies, educators can foster a love of learning in children and help them develop a strong foundation in Roman numerals, setting the stage for future academic success.
Roman Numerals in Different Cultures
While Roman numerals originated in ancient Rome, their influence has spread across the globe, impacting various cultures and societies. The adoption and adaptation of Roman numerals in different cultural contexts highlight their versatility and enduring appeal.
Examples of Roman numerals in different cultures include:
- European Traditions: Roman numerals have been widely used throughout Europe, particularly in countries with strong historical ties to the Roman Empire, such as Italy, France, and Spain.
- Asian Influence: In some Asian cultures, Roman numerals are used in specific contexts, such as on clock faces or in academic settings, reflecting a blend of Western and Eastern traditions.
- Global Commerce: The use of Roman numerals in international trade and commerce, such as in the numbering of product models or editions, underscores their universal recognition and acceptance.
By examining the role of Roman numerals in different cultures, we can gain a deeper understanding of their global impact and appreciate the ways in which they have been embraced and adapted across diverse societies.
The Future of Roman Numerals
The future of Roman numerals is an intriguing topic, as they continue to hold a place in modern society despite the prevalence of the Arabic numeral system. As technology and globalization continue to shape the world, the role of Roman numerals may evolve, but their historical and cultural significance ensures their continued relevance.
Potential future developments for Roman numerals include:
- Digital Integration: The use of Roman numerals in digital interfaces and applications, such as in typography and design, may increase as designers seek to blend tradition with modernity.
- Educational Emphasis: As educators recognize the value of teaching Roman numerals, they may become an increasingly important component of curricula, promoting historical awareness and mathematical skills.
- Cultural Preservation: Efforts to preserve cultural heritage may lead to renewed interest in Roman numerals, ensuring their continued prominence in areas such as art, architecture, and literature.
While the exact trajectory of Roman numerals remains uncertain, their enduring appeal and historical significance suggest that they will continue to play a role in shaping our cultural landscape for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the value of VIX in Roman numerals?
The value of VIX in Roman numerals is 14. This is determined by adding the value of V (5) to the result of subtracting I (1) from X (10), which equals 9.
Why are Roman numerals still used today?
Roman numerals are still used today because they offer a sense of tradition, formality, and aesthetic appeal. They are commonly seen in contexts such as clock faces, movie titles, and the naming of monarchs and popes.
How do you write 100 in Roman numerals?
100 is written as "C" in Roman numerals, which stands for "centum" in Latin, meaning one hundred.
Are Roman numerals used in mathematics?
While Roman numerals are not commonly used in modern mathematics due to the efficiency of the Arabic numeral system, they can still be found in certain historical or educational contexts.
What are the rules for writing Roman numerals?
The rules for writing Roman numerals involve a combination of addition and subtraction based on the order of the numerals. Smaller numerals placed before larger ones are subtracted, while those placed after are added. No numeral should be repeated more than three times in succession.
Where did Roman numerals originate?
Roman numerals originated in ancient Rome as a system for counting and conducting trade. They have since become integral to Western culture and are still used in various applications today.
Conclusion
Roman numerals, with their rich history and enduring appeal, continue to captivate and intrigue people around the world. From their origins in ancient Rome to their applications in modern society, Roman numerals have maintained their significance as a symbol of tradition and elegance. Understanding Roman numerals, particularly combinations like VIX, requires a grasp of the fundamental principles of this ancient system. By exploring their historical context, cultural impact, and practical applications, we can appreciate the enduring legacy of Roman numerals and their role in shaping our past, present, and future.
Article Recommendations